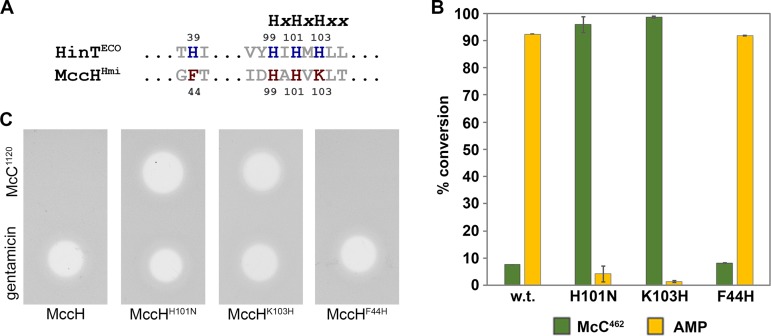
FIG 7.
Mutational analysis of active site residues of MccHHmi. (A) Sequence alignment of the conserved HIT motif of HinTEco and MccHHmi. (B) Phosphoramidase activity of MccHHmi active-site mutants. In vitro reaction mixtures containing aspartamide-adenylate McC462 were incubated with wild-type MccHHmi and the mutant proteins, containing the H101N or K103N substitution, and then analyzed by RP-HPLC. The conversion of McC462 was calculated as the percentage of McC462 and AMP absorption peak areas that remained after the reaction completion relative to the corresponding peak areas observed without the addition of enzymes. The bars represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) conversion percentages calculated from three independent measurements. (C) Mutations in the active center of MccHHmi abolish immunity to McC1120. Growth inhibition of E. coli cells harboring pBAD plasmids encoding the indicated proteins. Solutions (5 μM) of McC1120 and 0.5 μg/ml gentamicin were deposited on freshly prepared lawns and allowed to grow overnight at 37°C under conditions of induction of plasmid-borne genes.