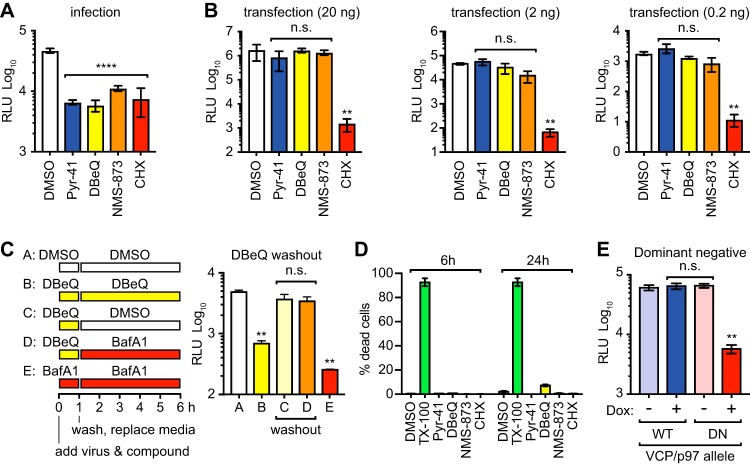
FIG 3.
VCP/p97 is essential for an early, postfusion stage of YFVΔSK/Nluc virus infection. (A) Nluc expression at 5 h postinfection with YFVΔSK/Nluc (MOI of 0.1) of BHK cells treated with Pyr-41 (50 μM), DBeQ (10 μM), NMS-873 (300 nM), or CHX (100 μg/ml). This experiment was performed in triplicate and is representative of five independent experiments; error bars represent SD from the mean. (B) Nluc expression at 5 h posttransfection with 20 ng (left panel), 2 ng (middle panel), or 0.2 ng (right panel) YFVΔSK/Nluc RNA in BHK cells treated with the indicated compounds, as described above. This entire experiment was performed twice. (C) Nluc expression at 6 h postinfection with YFVΔSK/Nluc (MOI of 0.1) in BHK cells continuously treated with DMSO carrier control, DBeQ, or BafA1, as well as cells treated with DMSO or DBeQ and subjected to washout conditions, as indicated in the left panel and detailed in Materials and Methods. This experiment was performed three times, each in triplicate, with similar results. (D) Drug toxicity was quantified by plotting the percentage of dead cells against various inhibitor or control treatments, as above, at the indicated time points. Statistical significance was calculated by using ordinary one-way ANOVA (****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant). This experiment was repeated twice with similar results. (E) Nluc expression at 6 h postinfection of Flp-In T-Rex-293 cells induced to express a WT or dominant negative (DN) allele of VCP/p97 for 24 h prior to infection. This experiment is representative of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.