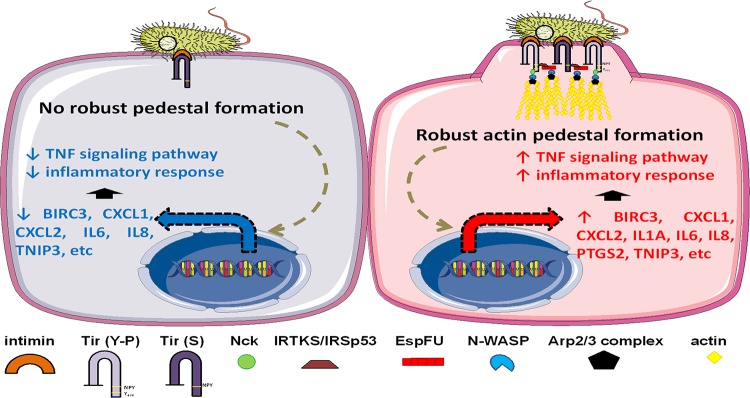
FIG 9.
Proposed model for the interaction of EPEC with the host epithelial cell. The formation of actin pedestals, especially when induced by EspFu-dependent mechanisms, activates inflammatory signaling pathways in the host cell. In the absence of a robust pedestal formation, most proinflammatory genes are downregulated, possibly due to the activity of translocated T3SS effectors which dampen the inflammatory response. Thus, the EPEC-induced inflammation is a balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory events.