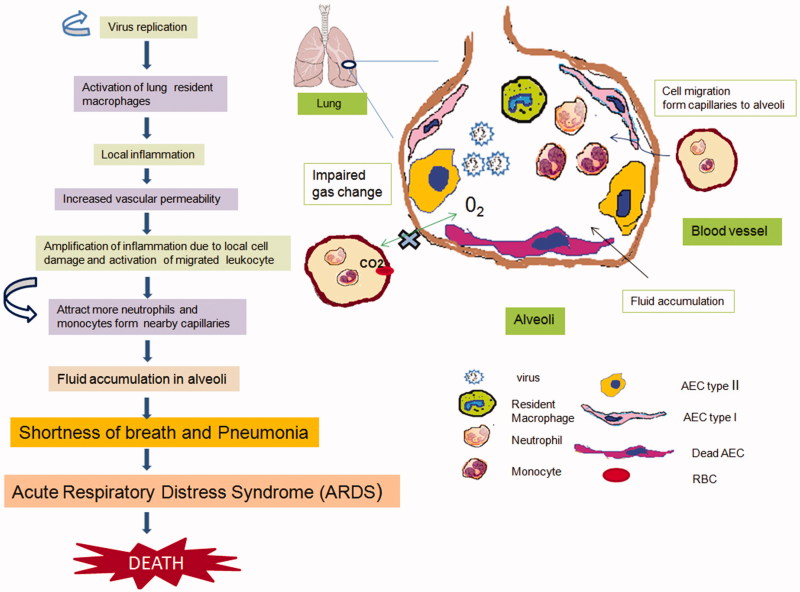
Figure 4.
Immunopathogenesis of Coronavirus infection. Robust viral replication in the lung causes activation of alveolar macrophages and epithelial cell damages which, results in the induction of inflammatory cytokines and release upon activation through innate immune receptors. Cyclic amplification of inflammatory responses lead to pneumonia and hypoxia as depicted in figure. Alveolar Epithelial Cells (AEC); Red Blood Cells (RBCs).