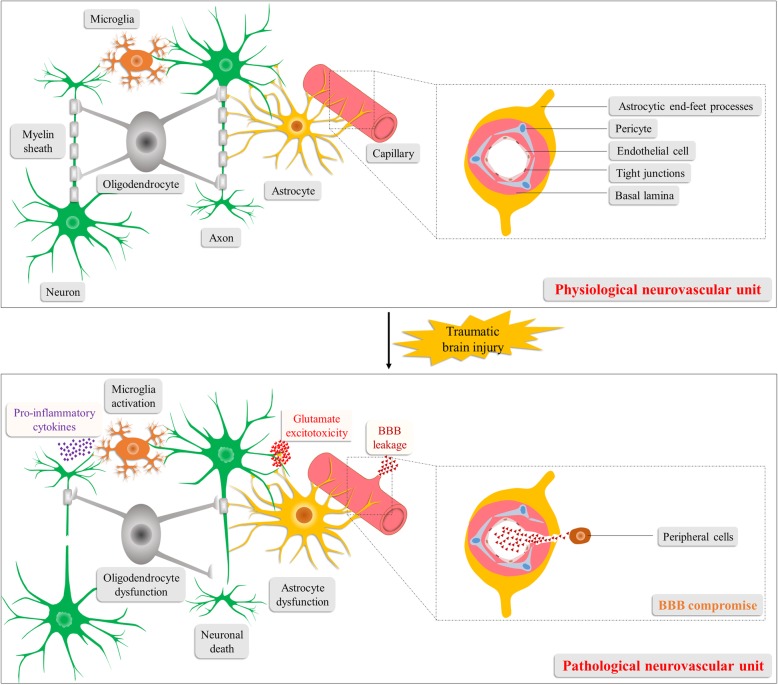
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the neurovascular unit under normal physiological conditions and TBI pathological conditions. The neurovascular unit encompasses neurons, glial cells (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and microglia), vascular cells (pericytes, endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells) and the basal lamina matrix. Following TBI, disruption of the neurovascular unit arises from and further aggravates the pathophysiological processes of TBI, which include BBB compromise, neuronal death, neuroglial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and metabolic disturbances