Figure 14-44.
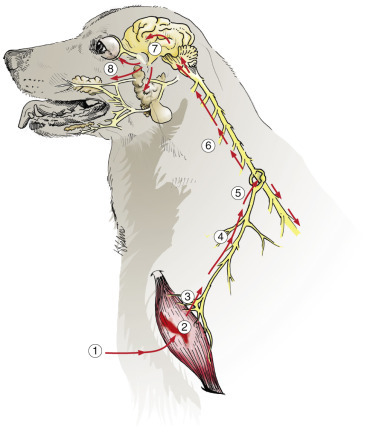
Pathogenesis of Rabies.
After a bite wound, 1, the rabies virus initially replicates in muscle (can enter peripheral nerves directly), 2, enters, 3, and ascends (retrograde axonal transport) the peripheral nerve, 4, to the dorsal root ganglion, 5, enters the spinal cord, 6, and ascends, 7, to the brain via ascending and descending nerve fiber tracts, infects brain cells, spreads to salivary glands, 8, and the eye and is excreted in saliva.
