Figure 14-95.
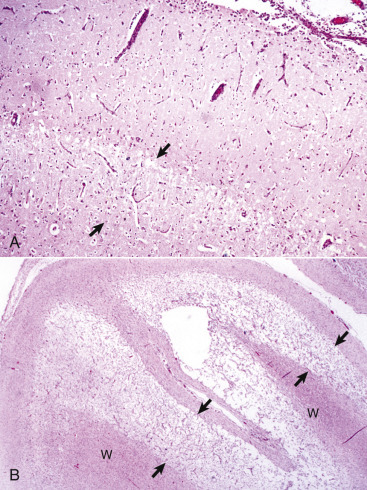
Polioencephalomalacia, Cerebral Cortex, Cross-Sectional View, Cow.
A, Acute stage. Note the zone of edema and acute neuronal necrosis affecting lamina 4-6 (area between arrows) of the cerebral cortex. Monocytes can be seen in the pia-arachnoid layer and subarachnoid space (upper right) in response to neuronal injury and the need to phagocytose cellular debris. Monocytes will also rapidly appear in perivascular spaces of blood vessels in the area of laminar edema and neuronal necrosis. H&E stain. B, Chronic stage. Areas of microcavitation in the deep cortical laminae next to the subcortical white matter are poorly stained (area between arrows) when compared with those of the normal superficial cortex (left). W, White matter. H&E stain.
(A courtesy Dr. W. Haschek-Hock, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Illinois. B courtesy Dr. J.F. Zachary, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Illinois.)
