Figure 14-104.
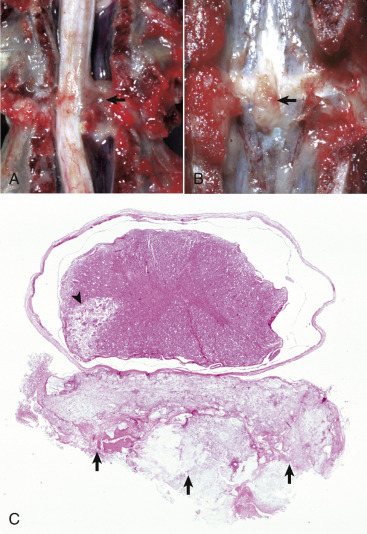
Intervertebral Disk Disease, Dog.
A, Disk rupture (herniated intervertebral disk), spinal cord compression. Disk material compresses the spinal cord (arrow) resulting in Wallerian degeneration. B, Vertebral column, lumbar vertebrae. Herniated intervertebral disk (arrow) protrudes into the vertebral canal. C, Herniated intervertebral disk, spinal cord. The disk material (arrows) lies in the epidural space, touches the dura mater, and compresses the overlying spinal cord. An area of necrosis, possibly caused by infarction, is present in the ventral area of the left lateral funiculus (arrowhead). The multiple small holes in all funiculi are the sites of lost nerves as the result of spinal cord compression, which caused Wallerian degeneration. H&E stain.
(Courtesy Dr. M.D. McGavin, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Tennessee.)
