Figure 25-9.
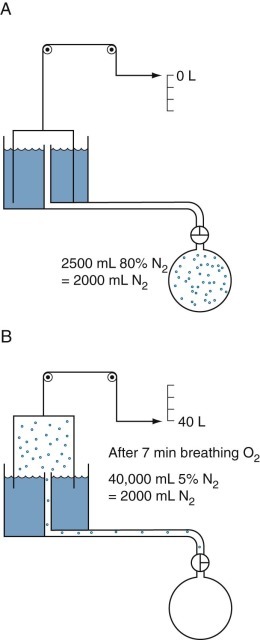
Open-circuit nitrogen method to measure functional residual capacity.
Dots represent nitrogen (N2) molecules. A, Initially all the N2 molecules are in the lungs (as 80% N2). B, When N2-free oxygen (“pure O2”) is breathed, the N2 molecules are washed out of the lungs and collected with the O2 as expired gas in the spirometer. The spirometer contains 40,000 mL of mixed expired gas with a N2 concentration of 5%. Thus the spirometer contains 0.05 × 40,000 = 2000 mL of N2; the remaining 38,000 mL of gas is mainly O2 used to wash the nitrogen out of the lungs, plus some carbon dioxide. The 2000 mL of N2 was distributed within the lungs at a concentration of 80% N2 when the washout began; therefore the alveolar volume in which the N2 was distributed was 2000/0.8 mL = 2500 mL. Corrections must be made for the small amount of N2 washed out of the blood and tissue when O2 is breathed and for the small amounts of N2 in “pure O2.”
