eFigure 25-11.
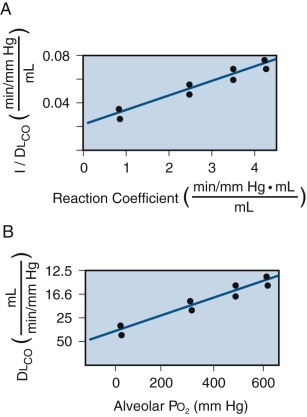
Subdivisions of the Dlco.
Experimental values of the diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DlCO) obtained at different alveolar Po2 values (x-axis in B) can be analyzed mathematically to obtain the subdivisions of total DlCO: the diffusing capacity of the membrane (Dm) and pulmonary capillary blood volume (Vc). As the alveolar Po2 was increased from 40 mm Hg to 600 mm Hg, the duplicate measurements of DlCO decreased from approximately 45 to 15 mL/min per mm Hg. Changing alveolar Po2 changes the reaction coefficient (θ), reflecting the change in hemoglobin affinity for carbon monoxide. The reaction coefficient is plotted against 1/DlCO in A. There is a linear relationship between 1/DlCO and 1/θ such that 1/DlCO = 1/θVc + 1/Dm. Under these conditions, Dm is derived from the value of the y-intercept and Vc from the slope of the line.
