eFigure 25-20.
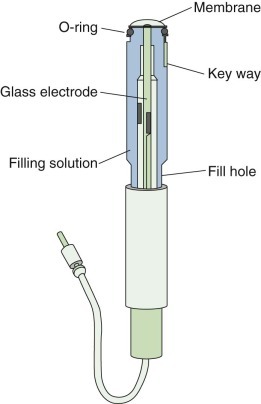
The structure of a carbon dioxide electrode.
This electrode uses the combination of the relationship between Pco2 and pH in a buffered solution and the design of a pH electrode. The sample is separated from a buffer solution by a membrane permeable to carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide molecules diffuse through the membrane, altering the concentration of carbonic acid, and therefore the hydrogen ion concentration in the buffered solution. The change in pH is read by a pH meter with output scaled in terms of Pco2.
