Figure 8.
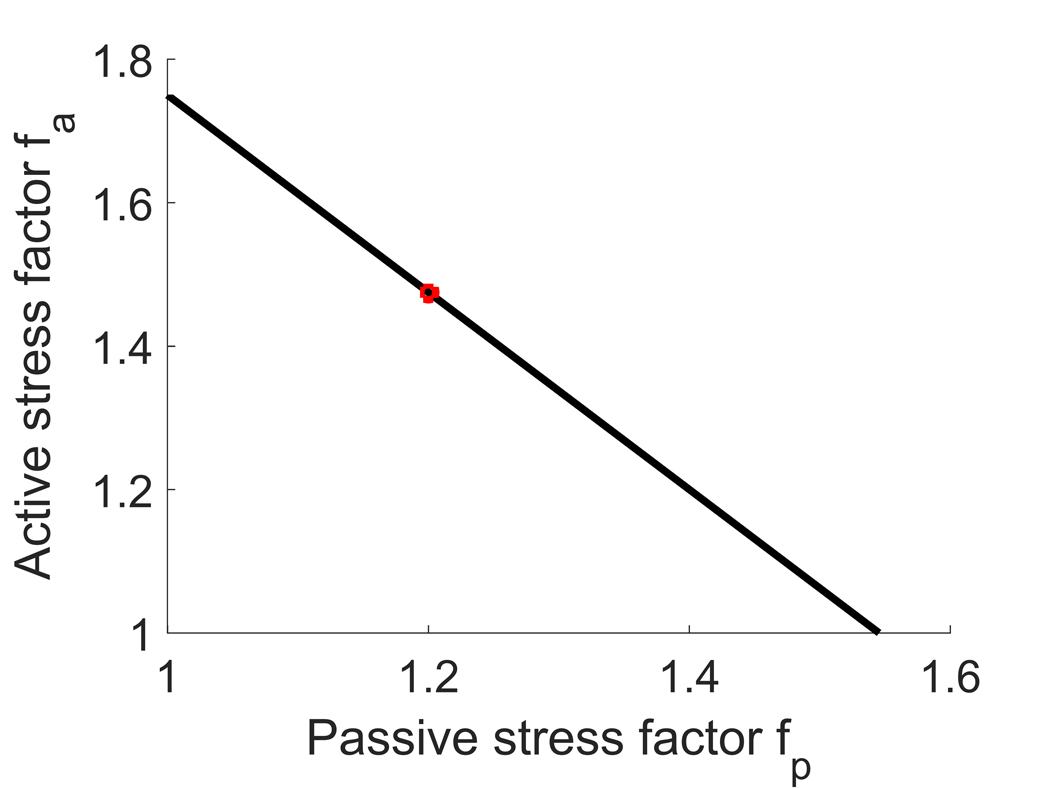
Plot of the critical pressure (above) and additional pressure (below) vs increase in passive response in vasospasm at 50% stenosis. The critical pressure is defined as the amount of pressure necessary to be applied to the arterial wall to reach the dilatation threshold, while the additional pressure is the amount of pressure an interventional device should provide to reach such dilatation threshold. Equivalently, the additional pressure equals the critical pressure after subtraction of systolic blood pressure (16 kPa). The case considered in the main text is shown in red.
