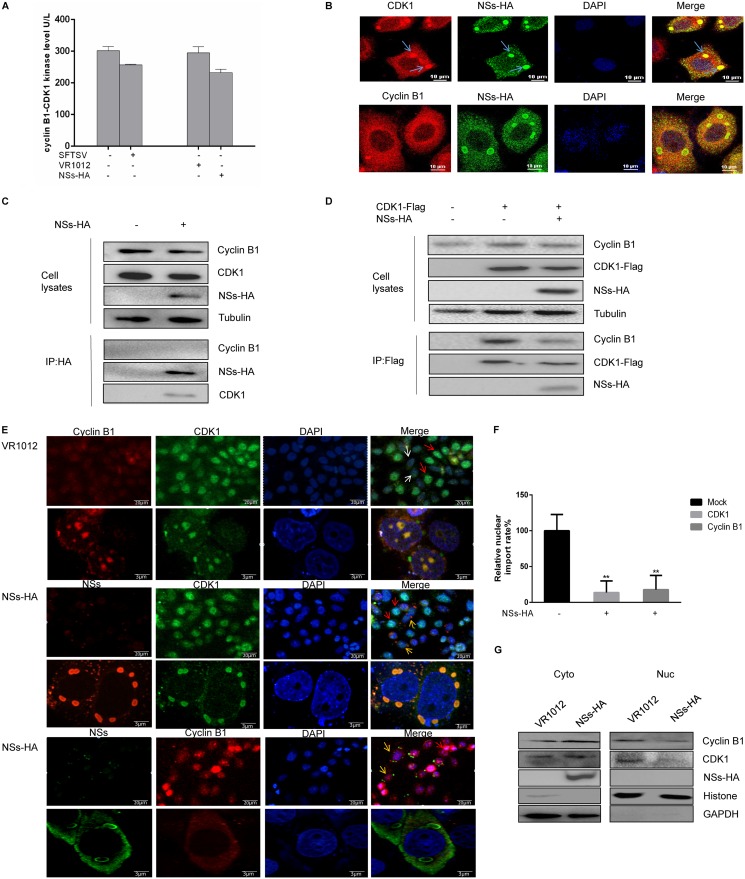
FIG 5.
NSs interacts with CDK1 and inhibits the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex from entering the nucleus. (A) HeLa cells were infected with SFTSV (10 MOI) or transfected with a plasmid encoding NSs-HA for 48 h, after which the cyclin B1-CDK1 level was measured using a human CDK1/cyclin B kinase expression level detection kit. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding NSs-HA. After 48 h, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and incubated with antibodies. A laser confocal microscope was used to observe colocalization of cyclin B1 with NSs, CDK1, and NSs. (C) 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding VR1012 or NSs-HA and collected at 48 h. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed to detect interactions between cyclin B1, CDK1, and NSs. (D) 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding VR1012 alone, VR1012 and CDK1-Flag, or NSs-HA and CDK1-Flag. The cells were collected at 48 h, and the effect of NSs on formation of the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex was analyzed by immunoprecipitation. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids encoding VR1012 or NSs-HA. After 48 h, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and incubated with antibodies. Localization of cyclin B1 and CDK1 to the nucleus was observed by confocal laser microscopy. The blue arrows indicate colocalization of NSs and CDK1, the red arrows indicate the nuclear cyclin B1-CDK1 complex, the white arrows indicate the cytoplasmic cyclin B1-CDK1 complex, and the yellow arrows indicate cells expressing NSs in which the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex localized to the cytoplasm. (F) Gen5 software was used to perform a statistical analysis of localization of the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex to the nucleus (**, P < 0.01). (G) 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding VR1012 or NSs-HA and collected at 48 h. Localization of the cyclin B1-CDK1 complex was determined by nuclear separation and Western blotting.