Fig. 4. (a).
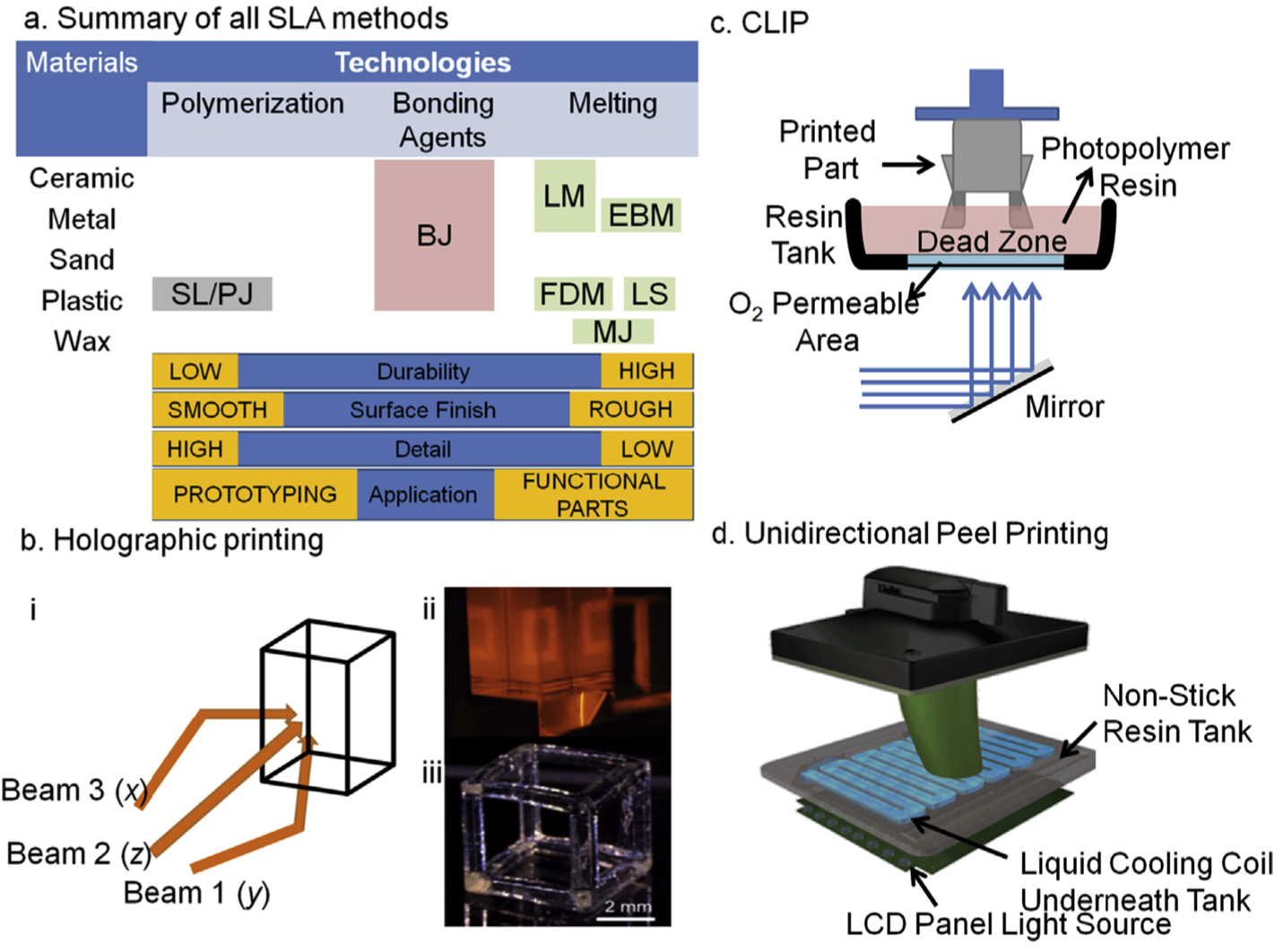
Illustrates a summary of different approaches for 3D printing with their print qualities. Binder Jetting: BJ; Electron Deposition Modeling: EDP; Fused Deposition Modeling: FDM; Hybrid Process: HP; Laser Melting: LM; Laser Sintering; Material Jetting: MJ; Photopolymer Jetting: PJ; Stereolithography: SL. (b) An overview of 3 dimensional light projection scheme in Holographic 3D printing set up (i) while in panel (ii) actual light projections of squares can be seen from all three planes that will create a hollow cube as depicted in a single projection of light as shown in panel (iii), a video related to this technology can be find at (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=00H-hXufpQE). (c) Depicts Continuous Liquid Interface Production scheme, which uses a combination of oxygen-based quenching of the reactive photoinitiator, allowing rapid printing within few minutes (15–20 min). (d) A set up of recently developed UDP method by Uniz Technologies, which is basically the fastest 3D printer in all segments. This is an arrangement of peeling in only z-direction by introducing a cooling coil in the otherwise non-sticky resin vat. The cooling causes peeling of the cured parts which also minimizes polymer shrinking due to hot-cold cycles.
