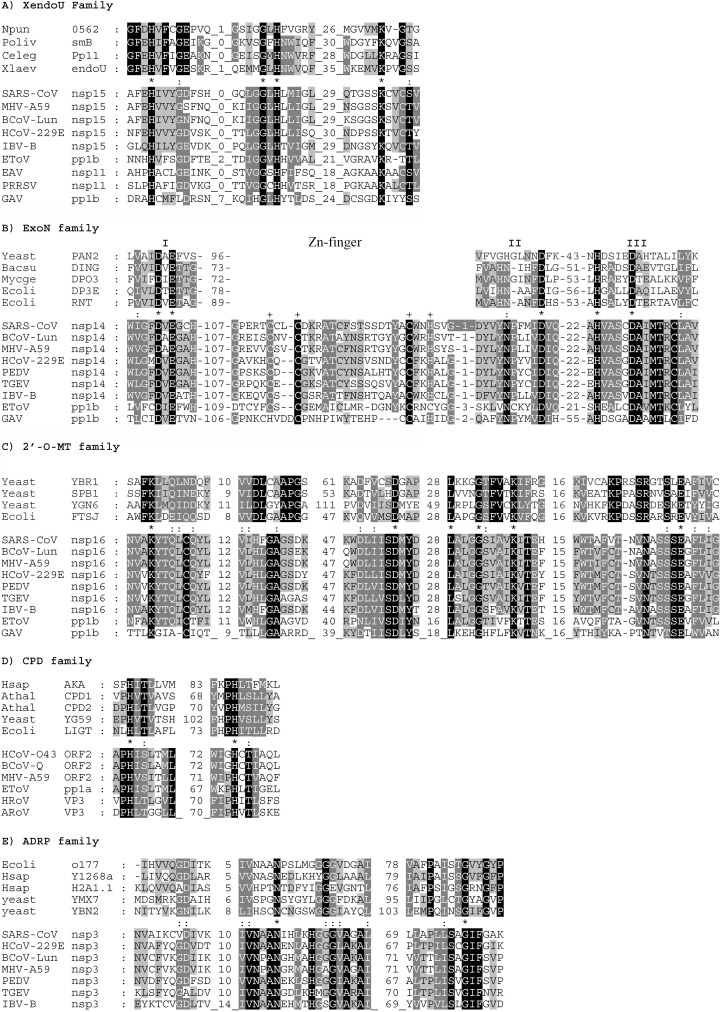
Figure 4.
Sequence alignments of protein families that include cellular enzymes involved in RNA processing and their nidovirus homologs. Our in-depth comparative sequence analysis (see Materials and Methods) revealed a statistically significant relationship between functionally uncharacterized proteins (domains) of nidoviruses, including SARS-CoV, and five protein families that include enzymes involved in two nuclear RNA processing pathways: intron excision to produce mature tRNA58 and the production of intron-encoded box C/D small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) from its host pre-mRNA (Figure 5).59 Shown are alignments for key regions of a few selected members of the following groups of enzymes: (A) XendoU family; (B) ExoN family; (C) 2′-O-MT family; (D) CPD family; and (E) ADRP family. These protein families may be known also under other names. Cellular homologs, not necessarily including proteins involved in the discussed RNA processing pathways, are listed in the top segment of each alignment and nidovirus proteins in the bottom segment. In the CPD family, along with group 2 coronavirus representatives, proteins of two rotaviruses (double-stranded RNA viruses), which were identified in this study, are listed. In both segments, residues are highlighted independently: black for absolutely conserved residues and different shades of grey to indicate different levels of conservation; amino acid similarity groups used were: (i) D, E, N, Q; (ii) S, T; (iii) K, R; (iv) F, W, Y; and (v) I, L, M, V. Positions occupied by identical or similar residues in all proteins under comparison are indicated with an asterisk (∗) and colon (:), respectively, in the inter-segment row. For the ExoN family, three motifs conserved in the DEDD superfamily and Zn-finger unique for the ExoN family are indicated. Database accession numbers for nidovirus genome sequences: SARS-CoV, Entrez Genomes accession number NC_004718 (AY274119); MHV-A59, NC_001846; BCoV-Lun, AF391542; HCoV-229E, NC_002645; IBV-B, NC_001451; PEDV, NC_003436; TGEV, NC_002306; equine torovirus (EToV), X52374; equine arteritis virus (EAV), X53459; porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), M96262; gill-associated virus (GAV), AF227196. Abbrevations and NCBI protein database ID number or SwissProt names of the remaining protein sequences are: (A) Npun 0562, hypothetical protein of Nostoc punctiforme, ZP_00106190; Poliv smB, pancreatic protein of Paralichthys olivaceus, BAA88246; Celeg Pp11, placental protein 11-like precursor of Caenorhabditis elegans, NP_492590); Xlaev endoU, endoU protein of Xenopus laevis, CAD45344; pp1b, ORF1b-encoded part of nidovirus replicase polyprotein 1ab. (B) Yeast PAN2, PAB-dependent poly(A)-specific ribonuclease subunit PAN2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, P53010; Mycge DPO3, DNA polymerase III polC-type, containing exonuclease domain, of Mycoplasma genitalium, P47277; Bacsu DING, probable ATP-dependent helicase dinG homolog, containing exonuclease domain, of Bacillus subtilis, P54394; Ecoli DP3E, DNA polymerase III, epsilon chain, containing exonuclease domain, of Escherichia coli, P03007 (PDB: 1J53 and 1J54); Ecoli RNT, exoribonuclease T of Escherichia coli, P30014. (C) Hsap AKA, A-kinase anchoring protein 18 gamma of Homo sapiens, AAF28106; Athal CPD1, putative CPD1 of Arabidopsis thaliana, CAA16750; Athal CPD2, putative CPD2 of Arabidopsis thaliana, CAA16751; yeast YG59, hypothetical 26.7 kDa protein of yeast, P53314; Ecoli LIGT, 2′-5′ RNA ligase of Escherichia coli, P37025; ns2, non-structural protein (ORF2-encoded) of the coronaviruses HCoV-O43 (AAA74377), BCoV-Quebec (P18517), and MHV-A59 (P19738); EToV pp1a, C-terminal fragment of EToV pp1a, S11237; HRoV VP3, VP3 of human rotavirus, BAA84964; ARoV VP3, VP3 of avian rotavirus PO-13, BAA24128. (D) Ecoli o177, putative polyprotein of Escherichia coli, AAC74129; Hsap Y1268a, KIAA1268 protein of Homo sapiens, BAA86582; Hsap H2A1.1, histone macroH2A1.1 of Homo sapiens, AAC33434; yeast YMX7, hypothetical 32.1 kDa protein of yeast, Q04299; yeast YBN2, hypothetical 19.9 kDa protein of yeast, P38218. (E) Yeast YBR1, putative ribosomal RNA methyltransferase (rRNA (uridine-2′-O-)-methyltransferase) of yeast, P38238; yeast SPB1, putative rRNA methyltransferase SPB1 of yeast, P25582; yeast YGN6, putative ribosomal RNA methyltransferase YGL136c (rRNA (uridine-2′-O-)-methyltransferase) of yeast, P53123; Ecoli FTSJ, cell division protein of Escherichia coli, NP_417646.