Figure 6.
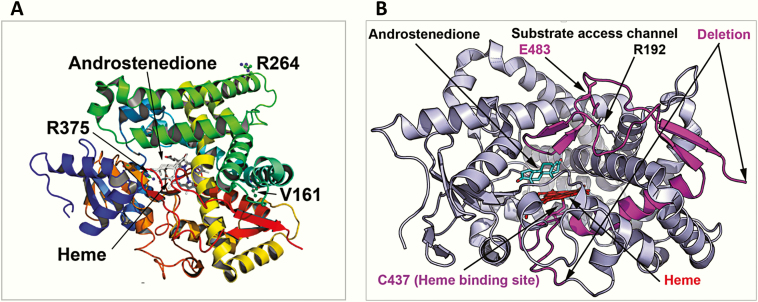
Structural location of CYP19A1 variants. A, Point mutations. Here a ribbons model of CYP19A1 protein colored in the rainbow from amino terminus (violet) to carboxy terminus (red) is shown and the bound substrate, androstenedione, and central heme molecule are depicted as stick models. Heme is ligated to the protein via cysteine 437 residue and forms the catalytic center of the CYP19A1 protein. The substitution of valine 161 for aspartate introduces a buried charge and a hydrophilic residue in the core of the protein, which would cause reduced stability of the structure. The R264 residue on aromatase is surface exposed and located on the G helix of the CYP19A1 structure, which is part of the substrate access channel, and it has been widely reported to be flexible in cytochromes P450. The R375 residue is involved in binding of heme propionate at the catalytic center of the CYP19A1, and its change to cysteine will lead to loss of heme binding and a nonfunctional protein. B, Identified deletion/insertion variations. The P423_H503delins mutation results in loss of critical amino acids in aromatase, including the heme ligating cysteine 437, and would, therefore, result in an inactive enzyme that would also be unstable and subject to degradation.