Figure 4.
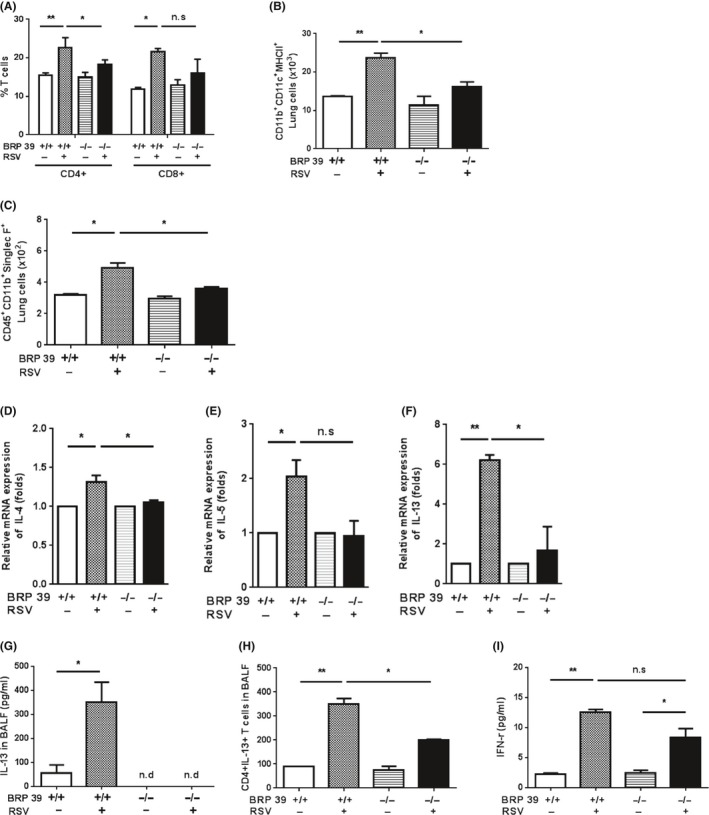
Breast regression protein‐39 (BRP‐39) regulates activation of Th2 inflammation. Lung tissue from each group was analyzed by flow cytometry. A, CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts were higher in the wild‐type (WT) respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) group and CD4+ T cell counts were lower in BRP‐39 knockout (KO) mice. B, DCs were detected by staining with anti‐CD11b, ‐CD11c, and –MHC II antibodies. In the absence of BRP‐39, the number of DCs was decreased relative to RSV‐infected WT mice. C, Eosinophil counts were higher in the lungs of RSV‐infected WT as compared to BRP‐39 KO mice. D‐F, Th2 cytokine mRNA levels were determined by RT‐PCR. IL‐13 level was elevated in RSV‐infected WT mice, whereas Th2 cytokine expression was not significantly increased by RSV infection in BRP‐39 KO mice. G, IL‐13 level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was increased in WT RSV mice, as determined by ELISA. H, IL‐13 expression was evaluated in CD4+ T cells in BALF. I, IFN‐γ production was increased in BALF after RSV infection in both WT and BRP‐39 KO mice, as determined using a cytokine bead array. n.d., not detected; n.s., not significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,
