Figure 2.
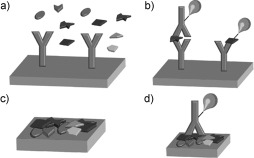
Schematic representation of forward‐phase protein arrays (FPPAs) and reverse‐phase protein arrays (RPPAs). a) In an FPPA, a specific protein of a sample that contains a variety of proteins is captured by specific antibodies immobilized in different spots on the microarray. Each array is incubated with one sample. b) Either a labeled second antibody (left) or a labeled analyte protein (right) is used for readout in an FPPA. Multiple analyte endpoints are detected for one sample. c) In an RPPA, a sample (e.g. a patient sample or a cell lysate) containing a variety of proteins is spotted in a microarray format. On each spot of the array, a different sample is immobilized. Thus, hundreds of samples are contained in one microarray. d) For detection in an RPPA, only one labeled antibody, which is specific for a certain protein, is used for signal generation and amplification. Thus, an endpoint analysis for one analyte is monitored across hundreds of samples.
