Figure 2.
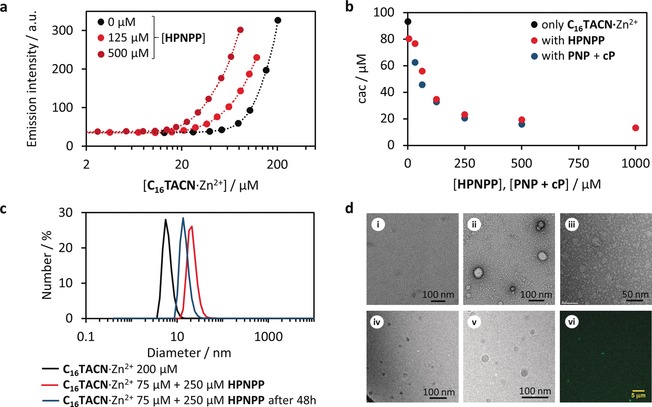
HPNPP templating ability. a) Selected emission intensity profiles for Nile red (5 μm, λ ex=570 nm, λ em=643 nm) at increasing C16TACN⋅Zn2+ concentrations, in the absence (black dots) and in the presence of HPNPP (125 μm, light red dots and 500 μm, dark red dots); the dotted lines serve as guide for the eye; b) Critical assembly concentration of C16TACN⋅Zn2+ measured in the presence of different concentrations of HPNPP or waste products (PNP + cP) with Nile red as a fluorescent probe. c) Hydrodynamic diameter of assemblies measured with dynamic light scattering (DLS) in the absence of HPNPP (black line) and in the presence of HPNPP (red line) and in the presence of waste (PNP + cP). d) Representative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of (i) [C16TACN⋅Zn2+]=50 μm in the absence of substrate HPNPP; (ii) vesicles obtained with [C16TACN⋅Zn2+]=50 μm in the presence of HPNPP (250 μm) and (iii) structures formed with [C16TACN⋅Zn2+]=50 μm in the presence of waste; (iv) and (v) show representative cryoTEM images with [C16TACN⋅Zn2+]=50 μm and [HPNPP]=250 μm; (vi) shows a representative image of vesicles with confocal microscopy for samples prepared with [C16TACN⋅Zn2+]=75 μm, [HPNPP] 250 μm and [coumarin 153]=1 μm. All experiments were performed in aqueous buffer solution (HEPES, 10 mm, pH 7.0) at 25 °C and standard TEM images were stained with 1 % uranyl acetate solution.
