Figure 5.
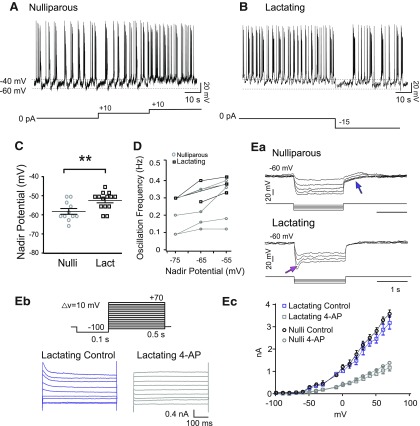
Lactation-associated increase in oscillation frequency is paralleled by depolarization and changes in TIDA membrane properties. A, Whole-cell current-clamp in vitro recording of a DAT-GCaMP3 neuron in the dmArc from a nulliparous female. Membrane potential alternates between hyperpolarized DOWN states and depolarized UP states crowned by action potential discharge. Note increasing frequency of oscillations as depolarizing current of increasing amplitude is injected (10 pA steps). B, Current-clamp recording of a DAT-GCaMP3 neuron from a lactating female. Note faster oscillation frequency that slows down on injection of hyperpolarizing current (−15 pA step). C, The mean DOWN state potential (nadir) of DAT-GCaMP3 dmArc neurons from lactating females is more depolarized (−54.00 ± 1.87 mV; n = 10) than in virgin females (−60.00 ± 1.15 mV; n = 11). **p < 0.01 (unpaired Student's t test). D, Nadir potential plotted against oscillation frequency (data from whole-cell recordings in DAT-GCaMP3 neurons). Note linear relationship in both nulliparous and lactating females, and overall higher oscillation frequencies in lactating dams. Ea, Electrophysiological recordings of DAT-GCaMP3 neuron from a nulliparous (top) and lactating (below) female in the presence of TTX (500 nm), to abolish oscillations and establish a stable baseline, in response to a series of hyperpolarizing square current steps (−10/−20 to −50 pA). Blue arrow indicates outwardly rectifying (A-like) current. Note depolarizing sag in lactating female (absent from nulliparous control), indicative of the h-current (Ih, magenta arrow). Eb, Representative traces from a whole-cell voltage-clamp recording from DAT-tdTomato neuron in the dmArc from a lactating dam before and after 4-AP application (4 mm) application. Command voltage protocol to elicit A-like K+ current shown above. A-type currents were evoked in response to 10 mV membrane potential steps from −80 to 70 mV after a −100 mV prepulse. Ec, Current–voltage curves from nulliparous and lactating dams in the presence or absence of 4-AP. No significant difference was found between control and 4-AP conditions (p = 0.08, F test; n = 5 for nulliparous; n = 6 for lactating).