Figure 4.
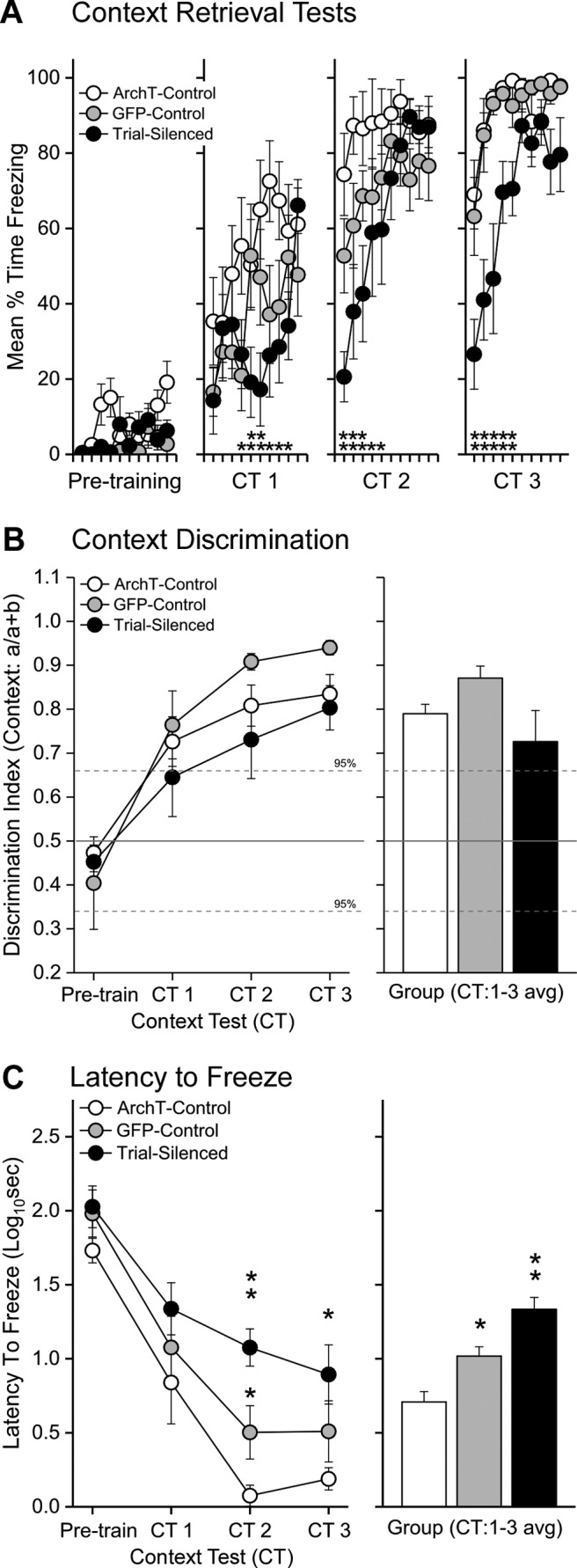
Silencing VH input to PL during training disrupts context fear learning. A, Each point represents the average (± SEM) freezing during each 30 s bin of the baseline period before training on day 1 (Pretraining) and during each context retention test (CT1-3, Days2-4) before training on each subsequent day. ArchT-controls (n = 8), GFP-controls (n = 8), and Trial-silenced (n = 7). VH-PL silencing during acquisition trials impaired the subsequent expression of freezing in the absence of laser and compared with ArchT- or GFP-controls during each retention test (CT1-CT3). *p < 0.05, significantly less freezing in the Trial-silenced group relative to ArchT-controls. **p < 0.05, significance from both ArchT- and GFP-controls during each 30 s bin; planned comparisons of a significant three-way interaction (F(54,540) = 2.47, p = 0.0000002; ηp² = 0.20). B, Context discrimination was delayed in the Trial group relative to GFP- and ArchT-controls. Each point represents the average ratio (± SEM) of context elicited freezing . An index > 0.5 indicates more freezing to the training context than to the CS testing context. Hatched lines indicate the ±95% CI above which indicates significant discrimination of fear. C, VH-PL silenced rats were slower to initiate freezing on each day of testing. Left, Each point represents the average latency to freeze (± SEM) during each session. *Significant Bonferroni-corrected contrasts, CT2-CT3 (p values < 0.005, Cohen's d = 3.654, 1.75). **Trial-silenced significantly slower than GFP-controls (p values < 0.004, Cohen's d: CT2 = 1.33, CT3 = 0.69, not significant). Right, Each bar represents the average latency to freeze (± SEM) across context testing. *Significant main effect of Group (F(2,21) = 21.96, p = 0.00001; ηp² = 0.68, ArchT-control < GFP-control < Trial-silenced, all p values < 0.0042).
