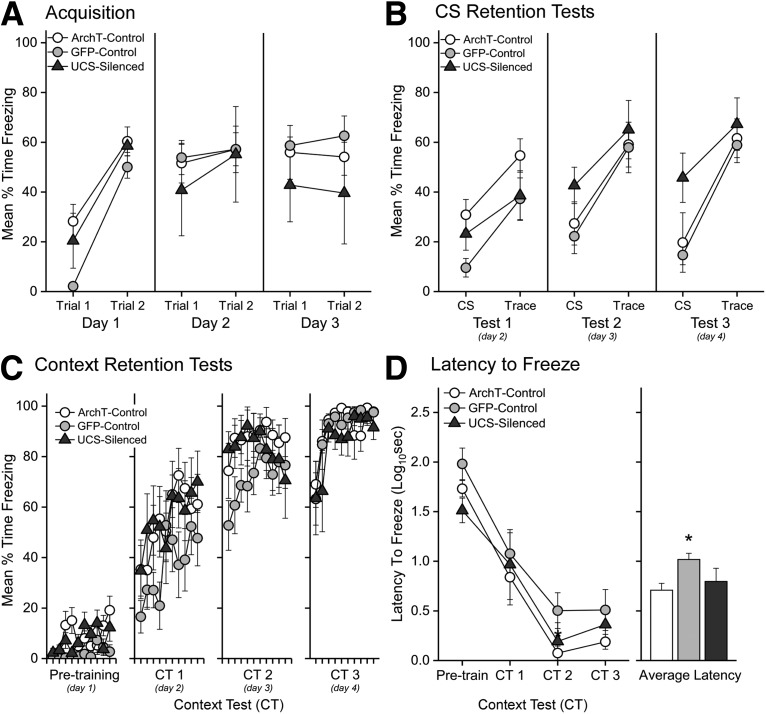
Figure 5.
Silencing VH input to PL during the UCS and postshock period does not impair trace or contextual fear learning. A-D, ArchT- and GFP-control data are redrawn from Figures 3 and 4. A, Each point represents the average freezing (± SEM) during the 10 s CS and 20 s trace interval on each trial of training (2 trials/day) for ArchT-controls (n = 8), GFP-controls (n = 8), and UCS-silenced (n = 4). B, Each point represents the average freezing (± SEM) during the 30 s CS and 30 s. Trace interval of the discrete CS test trials. C, Each point represents the average (± SEM) freezing during each 30 s bin of the Pretraining baseline period and subsequent CTs (CT1-CT3). ArchT-Control, GFP-control, and UCS-silenced rats exhibited similar freezing across days of testing. D, Graphs represent the average latency to freeze (± SEM) during each session (left) and average(± SEM) latency collapsed across days (right). Post hoc tests of a main effect of group (F(2,17) = 4.70, p = 0.02369, ηp² = 0.36) revealed that GFP rats were slower to initiate freezing compared with the viral ArchT-controls. *p < 0.05.