Fig. 4. PHF20L1 loss of function impairs the deposition of PRC2 and the NuRD complex, perturbing the balance of H3K27 modifications.
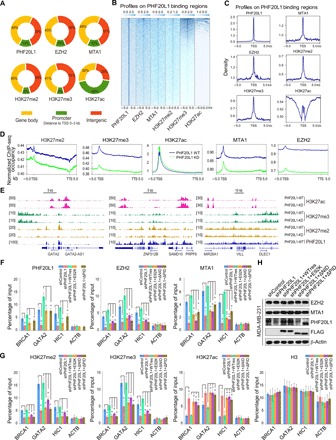
(A) Genomic distribution of PHF20L1, EZH2, MTA1, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, and H3K27ac ChIP-seq peaks. (B and C) ChIP-seq density heatmaps and profiles of EZH2, MTA1, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, and H3K27ac on PHF20L1 binding regions. TSS, transcription start site. (D) The average occupancy of EZH2, MTA1, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, and H3K27ac along the transcription unit in normal and PHF20L1 KD MDA-MB-231 cells. TTS, transcription termination site. (E) Visualized peaks at representative loci using an integrative genomics viewer. (F and G) qChIP analysis using specific antibodies against PHF20L1, EZH2, MTA1, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, H3K27ac, and H3 were performed in control, PHF20L1 KD, and PHF20L1 KD MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing shRNA-resistant PHF20L1 (represented as WTres), PHF20L1E98K, PHF20L1ΔNID, or PHF20L1ΔPID. ACTB served as control. (H) Western blotting analysis of EZH2 and MTA1 in cells as in (F and G). Data shown are means ± SD of triplicate measurements that have been repeated three times with similar results. Two-tailed unpaired t test, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (F and G).
