Figure 5: Approximate entropy (m=2, r=0.2SD, τ=1) vs. age and corresponding youngest vs. oldest quartile box plot for the (A) 0.5–30 Hz EEG range, (B) the EEG alpha range, (C) and the EEG beta range.
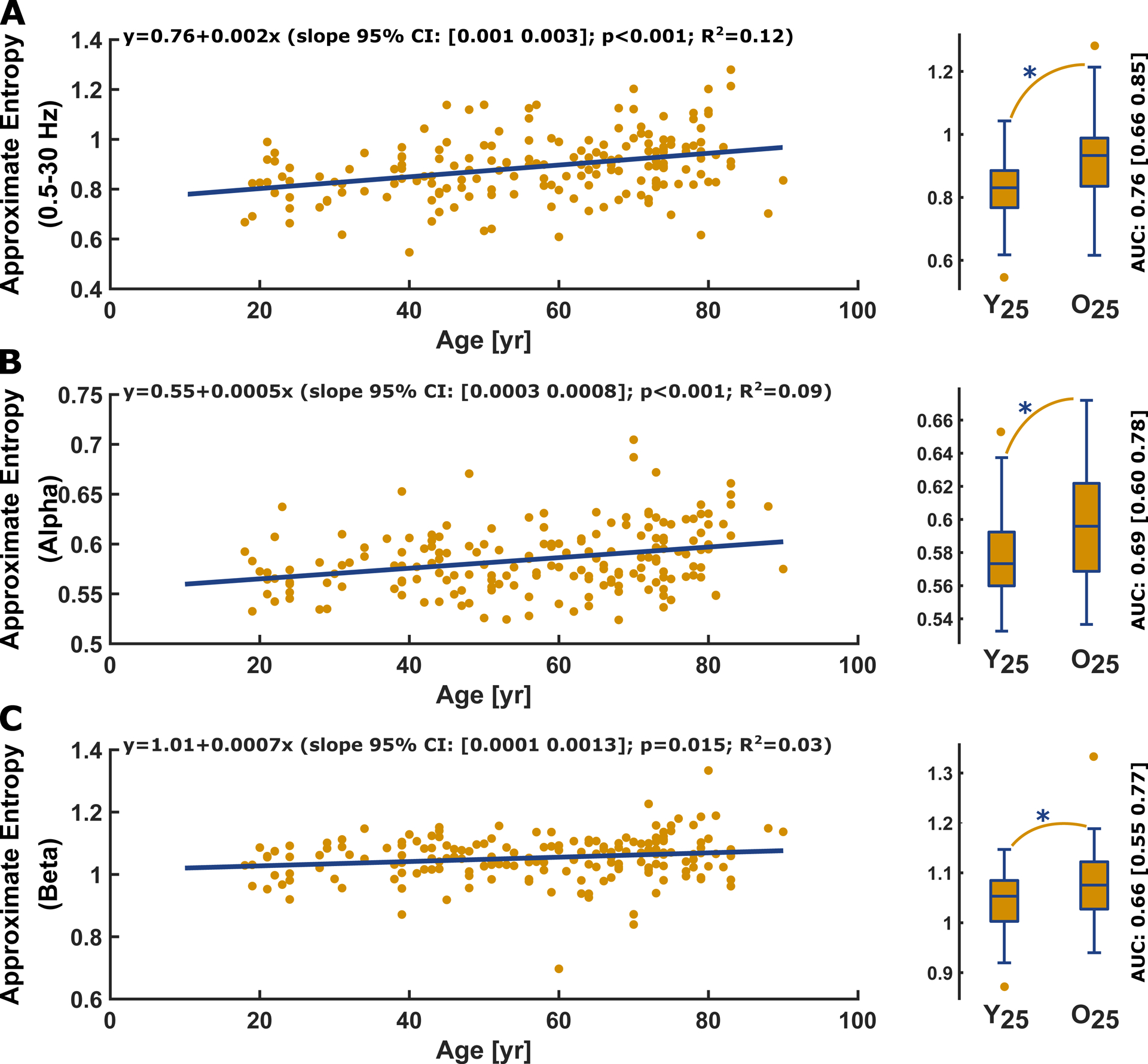
A) Approximate entropy of the 0.5–30 Hz filtered EEG significantly (p<0.001, t-statistic: 4.87) increased with age. Age had a “fair” and significant (p<0.001; AUC= 0.76 [0.66 0.85]) effect on approximate entropy as depicted in the comparison between Y25 (0.83 [0.77 0.89]) and O25 (0.93 [0.84 0.99]).
B) Approximate entropy of the alpha-band EEG significantly (p<0.001, t-statistic 4.18) increased with age. Age had a “poor”/”fair” and significant (p=0.002; AUC= 0.69 [0.60 0.78]) effect on approximate entropy as depicted in the comparison between Y25 (0.57 [0.56 0.59]) and O25 (0.60 [0.57 0.62])
C) Approximate entropy of the beta-band EEG significantly increased with age (p=0.015; AUC=0.66 [0.55 0.77]). Age had a “fair” and significant effect on approximate entropy as depicted in the comparison between O25 (1.08[1.03 1.12]) and Y25 (1.05 [1.00 1.08]) of the data set.
In the regression plots, the yellow dots present the single patients and the blue line the linear fit. In the boxplots, the circles indicate outliers as defined by the MATLAB plotting routine. They were not excluded from analysis. Y25: youngest 25% O25: oldest 25%; yr: year
