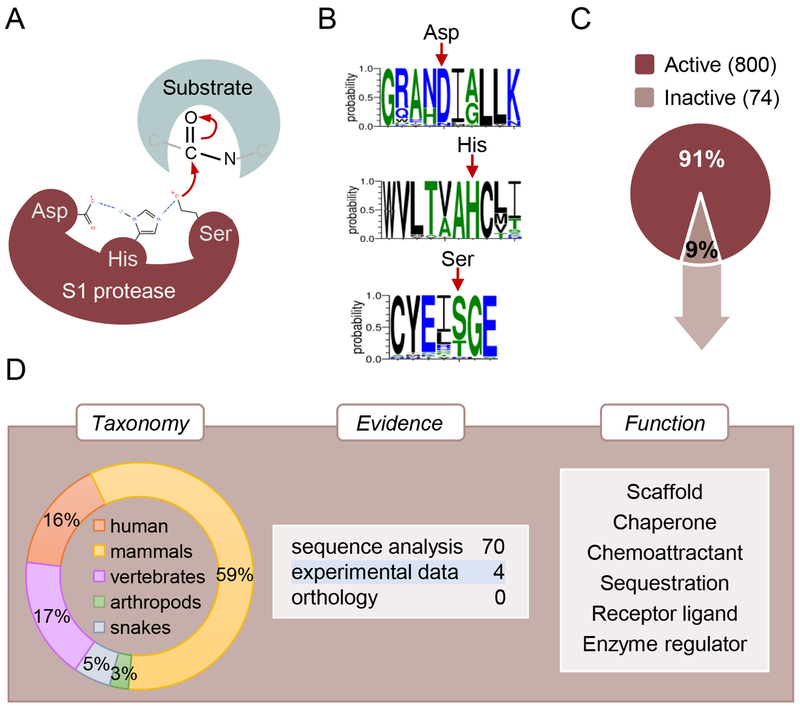
Fig. 2.
Serine pseudopeptidases. (A) Reaction mechanism and canonical catalytic triad residues (Asp/His/Ser) for the peptidase S1 family members. (B) Sequence logos of catalytic triad residues for 32 mammalian PRSS50 proteins. The red arrows indicate the position of the three catalytic residues. In rat Prss50 (UniProtKB D4A1L9), a serine residue acts as nucleophile whereas in human PRSS50 (UniProtKB Q9UI38) this role is performed by a threonine residue. (C) Analysis of UniProtKB reviewed members of the peptidase S1 family. The percentage of active and inactive proteases is shown. The number of active and inactive proteases is indicated in brackets. (D) Characterisation of the reviewed S1 pseudoproteases. Taxonomy distribution (left), evidence for lack of catalytic activity (middle) and function (right) are shown.