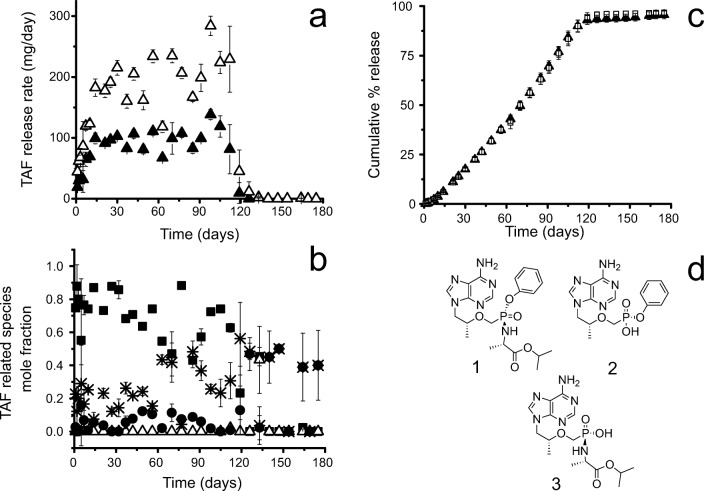
Fig. 8.
(a) Average daily release of TAF equivalent from 0.8 cm, 16.8 mg TAF (▲), and 1.6 cm 33.9 mg TAF (∆) implants used in animal PK and safety studies. Implants were made with Tecoflex™ EG-85A RCM (2.2 mm OD, 150 μm thickness) with a core pellet composition of 96:2:2 wt% TAF:NaCl:MgSt. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 10, n = 9 for 1.6 cm implant). (b) Average daily release of TAF parent (■) and TAF related species; PMPA monoamidate (*), monophenyl PMPA (∆) and TFV (●) from the same 0.8 cm implant above. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 10). Numeric values given in Table S-III. (c) Cumulative % release of TAF equivalent from 0.8 cm (▲) and 1.6 cm (□) implants. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 10, n = 9 for 1.6 cm implant). (d) TAF parent (1) is tenofovir alafenamide without the fumarate salt, which undergoes pH-dependent hydrolysis into two main related substances monophenyl PMPA (2) and PMPA monoamidate (3). These are the Generation A implants of the recent Su et al. (27).