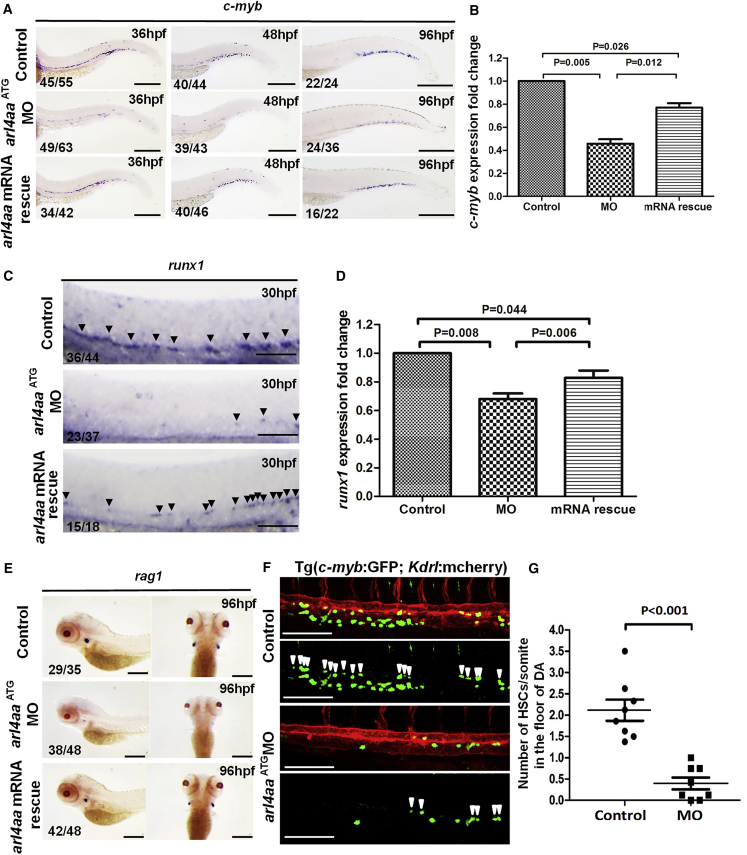
Figure 2.
Knockdown of Zebrafish arl4aa Perturbed Definitive Hematopoiesis
(A) c-myb expression in un-injected control (top), arl4aa morphant (MO) (middle), and morphant rescued by arl4aa mRNA (bottom) at 36 (left), 48 (middle), and 96 hpf (right).
(B) qRT-PCR of c-myb expression in control, MO, and arl4aa mRNA rescue groups (mRNA rescue) in embryos at 48 hpf. Data are representative of three independent experiments with error bars representing the mean ± SEM.
(C) runx1 expression at 30 hpf in un-injected control (top), arl4aa ( middle), and morphant rescued by arl4aa mRNA (bottom). Arrowheads indicate runx1-expressing cells in the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta (DA).
(D) qRT-PCR of runx1 expression in control, MO, and arl4aa mRNA rescue groups (mRNA rescue) in embryos at 30 hpf. Data are representative of three independent experiments with error bars representing the mean ± SEM.
(E) rag1 expression at 96 hpf between control (top), MO (middle), and arl4aa mRNA rescue groups (bottom).
(F) Confocal microscope imaging of double transgenic (cmyb:GFP; kdrl:mCherry) embryos injected with arl4aa MO. Arrowheads denote cmyb + kdrl + HSCs along the DA. The embryos were examined at 36 hpf.
(G) Number of HSCs at the floor of the DA per somite in Tg (cmyb:GFP; kdrl:mcherry) embryos at 36 hpf. The results are presented as mean ± SEM (p < 0.001; n = 8 embryos per group in three independent experiments). Scale bars, 250 μm (A) and 100 μm (C and E).
See also Figure S2.