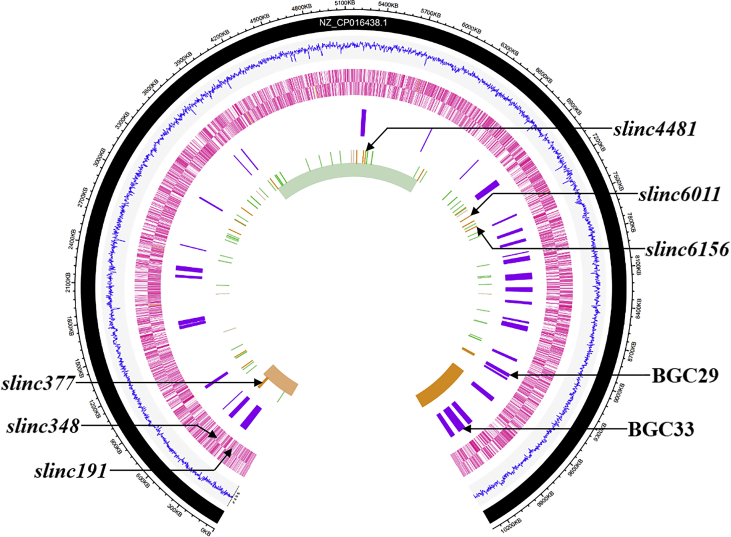
Fig. 3.
Chromosome map of genetic variations between B48 and NRRL 2936. From the outside in, circle 1: the chromosomal regions of NRRL 2936 (black); circle 2: G + C content of NRRL 2936 (blue); circles 3 and 4: (forward and reverse strands), the predicted protein coding genes (pink); circle 5: distribution of putative secondary gene clusters (purple); circle 6: positions of Indels (green for inserts and orange for deletions) and SNVs (plum for transition and pale green for transversion) between B48 and NRRL 2936; circle 7: positions of inversion (aquamarine) and duplication (sandy brown). Validated mutations that contributed to lincomycin overproduction are marked with arrows. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)