Figure 2.
Lineage-Tracing of Fetal C-KIT+ Cells Labeled a Few Chondrocytes in Fetus and a Subpopulation of SSCs in Adult Bone Marrow
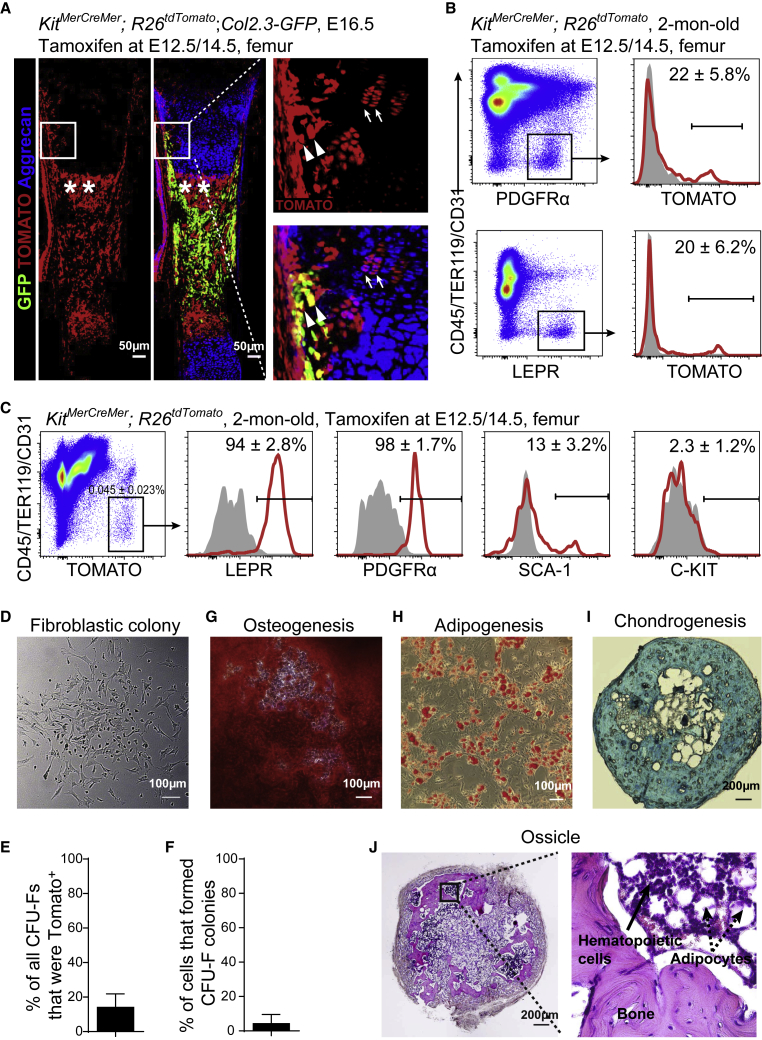
All KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato; Col2.3-GFP and KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice were tamoxifen treated at E12.5 and 14.5.
(A) Representative confocal images of femur sections from KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato; Col2.3-GFP mice at E16.5. Arrows indicated TOMATO+ chondrocytes at the growth cartilage; arrowheads indicated TOMATO+Col2.3-GFP+ preosteoblasts at the osteogenic perichondrium; asterisks indicated TOMATO+ stromal cells in the nascent primary ossification center in the bone marrow (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(B) Flow cytometric analysis showed that ∼22% of CD45−TER119−CD31−PDGFRα+ bone marrow stromal cells (upper plots) and ∼20% of CD45−TER119−CD31−LEPR+ bone marrow stromal cells (lower plots) were TOMATO+ in 2-month-old KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice. The corresponding bone marrow stromal cells from wild-type mice were set as negative controls (gray) (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(C) Representative flow cytometry plots of CD45−TER119−CD31−TOMATO+ bone marrow stromal cells from 2-month-old KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice. Isotype controls are shown in gray (n = 4 mice from four independent experiments).
(D) Representative bright-field image of colonies formed by TOMATO+ bone marrow stromal cells from 2-month-old KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(E) Percentage of all colonies from KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice that were TOMATO+. Macrophage colonies were excluded by staining with anti-CD45 antibody (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(F) Percentage of TOMATO+ bone marrow stromal cells from KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice that formed colonies in culture (n = 384 individual cells from 3 mice in three independent experiments).
(G–I) TOMATO+ CFU-Fs from 2-month-old KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice were able to differentiate into alizarin red S+ osteoblastic cells (G), oil red O+ adipocytes (H), and alcian blue+ chondrocytes (I). ∼500 TOMATO+ bone marrow stromal cells from KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice were cultured in colony-forming medium for 14 days. All colonies were digested and aliquots were cultured in osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation medium, respectively, before the staining. Adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation was performed in six-well plates while chondrogenic differentiation was performed as pellets in 15-mL tubes (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(J) Cultured TOMATO+ bone marrow stromal cells from 2-month-old KitMerCreMer; R26tdTomato mice were able to form bone ossicles upon subcutaneous transplantation (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).