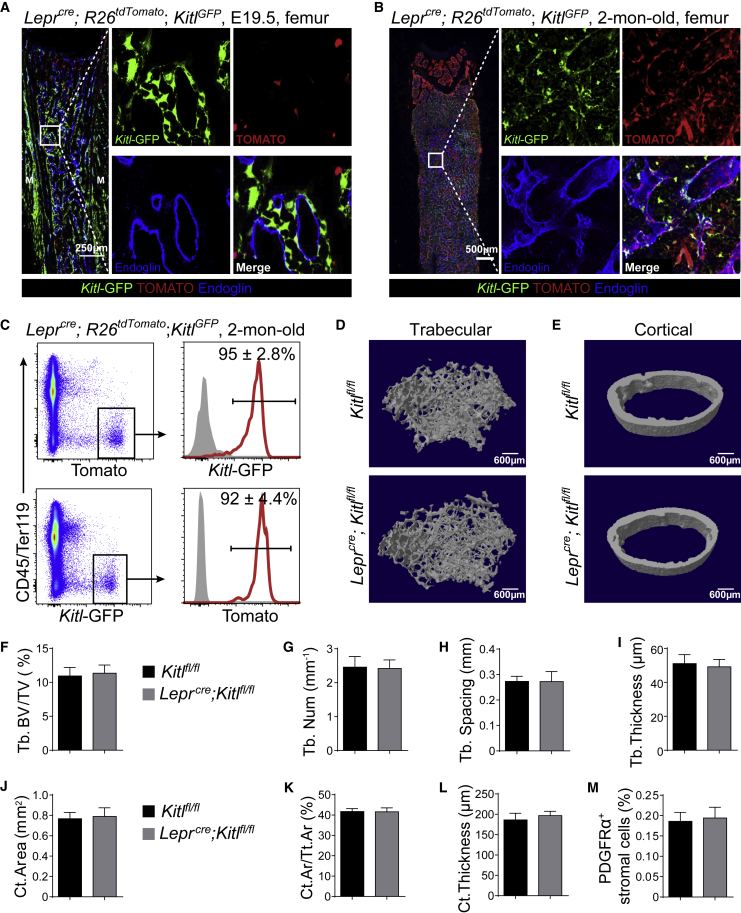
Figure 6.
Deletion of Kitl After Birth Did Not Affect Osteogenesis
(A and B) Representative confocal images of femur sections from Leprcre; R26tdTomato; KitlGFP mice at E19.5 (A) or 2 months of age (B). Bone marrow vessels were revealed by anti-ENDOGLIN staining (n = 3 mice/age from three independent experiments).
(C) Representative flow cytometry plots of enzymatically dissociated bone marrow cells from 2-month-old Leprcre; R26tdTomato; KitlGFP mice showed that most TOMATO+ cells were GFP+ and vice versa (n = 3 mice from three independent experiments).
(D and E) Representative microCT images showed trabecular bone (D) and cortical bone (E) from Kitlfl/fl and Leprcre; Kitlfl/fl mice (n = 5 mice per genotype from three independent experiments).
(F–L) MicroCT analyses of the trabecular bone volume/total bone volume (F), trabecular number (G), spacing (H), thickness (I), cortical area (J), cortical area/total area (K), and thickness (L) of femurs from Kitlfl/fl and Leprcre; Kitlfl/fl mice (n = 5 mice per genotype from three independent experiments).
(M) Frequencies of CD45−TER119−CD31−PDGFRα+ bone marrow stromal cells in Kitlfl/fl and Leprcre; Kitlfl/fl mice (n = 5 mice per genotype from three independent experiments). Two-tailed Student's t tests were used to assess the statistical significance of differences between sex-matched littermates in (F–M).