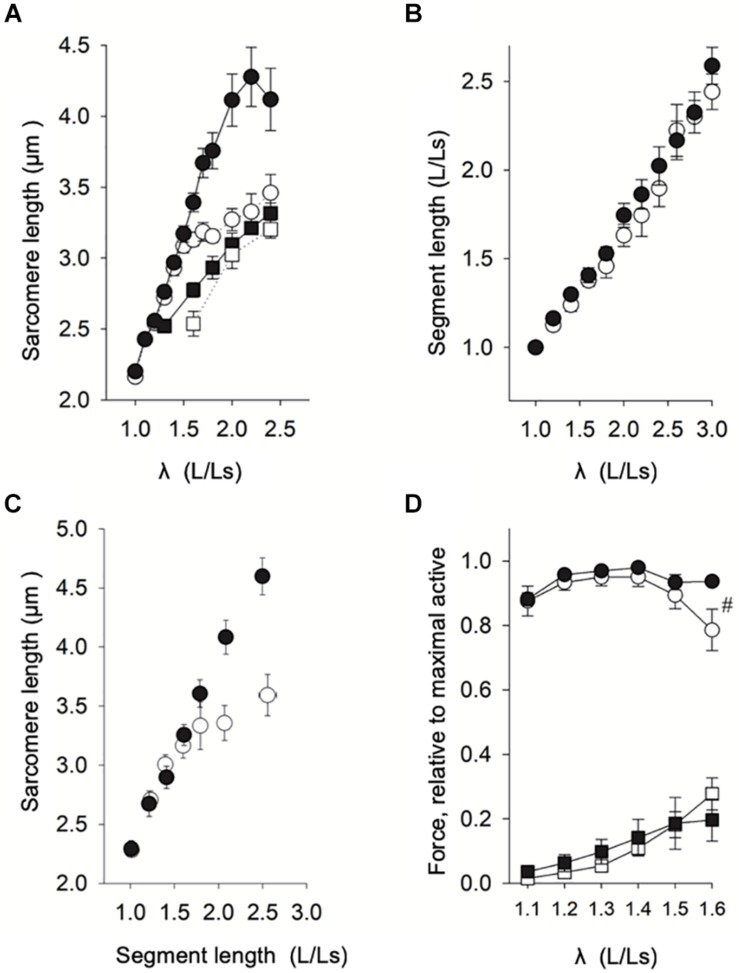
FIGURE 2.
Length-force analysis of woody and normal breast muscle. (A) Relation between muscle length (related to slack length, Ls) and sarcomere length in normal breast (open circles) and woody breast (filled circles) muscles (data from eight animals, 4–5 fibers each, grouped according to L/Ls, each L/Ls: n = 6–30). Filled squares show the relation of woody breast fibers compressed by 20% (to the same fiber diameter as that of normal breast fibers) using 4% dextran T-500, and open squares show the relation of normal breast fibers compressed by 20% using 4% dextran T-500. For L/Ls values ≥ 1.8, the sarcomere length of the woody breast group was significantly longer compared to normal muscle fibers (P < 0.05, Two-way ANOVA). (B) Relation between segment length, i.e., the distance between two carbon dots adhered to the fiber surface (relative to slack length, Ls, ∼60 μm), and muscle fiber length (relative to slack fiber length). (C) Relation between sarcomere length and segment length (relative to Ls) in normal (open circles) and woody (filled circles) muscle fibers (data from six animals, 2–3 fibers each, grouped according to segment length/Ls, n = 6–13). (D) Active (circles) and passive (squares) length-force relationships of normal (open symbols) and woody breast (filled symbols) fibers (average data from eight animals, 2–3 fibers each, grouped according to L/Ls, each L/Ls: n = 6–8). # Indicates significant difference in active force at L/Ls = 1.6 (P < 0.05).