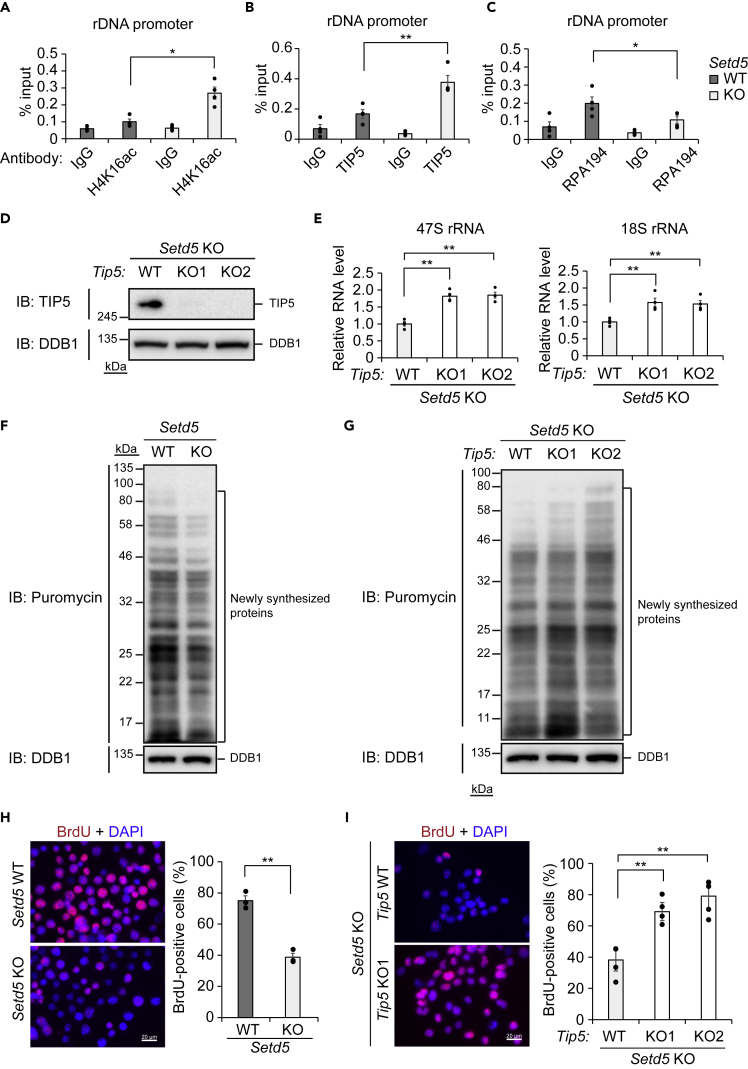
Figure 5.
Essential Role of TIP5 in Repression of rDNA in Setd5 KO Neuro2a Cells
(A–C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of H4K16ac (A), TIP5 (B), or RPA194 (C) at the rDNA promoter in WT or Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells. Data are means ± SEM (n = 4 independent experiments). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test).
(D) Immunoblot analysis of TIP5 in Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells with (KO1 and KO2) or without (WT) additional KO of TIP5.
(E) RT-qPCR analysis of 47S and 18S rRNA in Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells with or without TIP5 KO. Data are means ± SEM (n = 4 independent experiments). ∗∗p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test).
(F and G) Immunoblot analysis of translational activity on the basis of puromycin incorporation into newly synthesized proteins in WT or Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells (F) or in Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells with or without TIP5 KO (G).
(H and I) Immunofluorescence analysis (left) of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation in WT or Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells (H) or in Setd5 KO Neuro2a cells with or without TIP5 KO (I). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. The percentage of BrdU-positive cells was also determined for each condition (right). Data are means ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). ∗∗p < 0.01 by Student's t test (H) or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test (I).
See also Figures S8–S10.