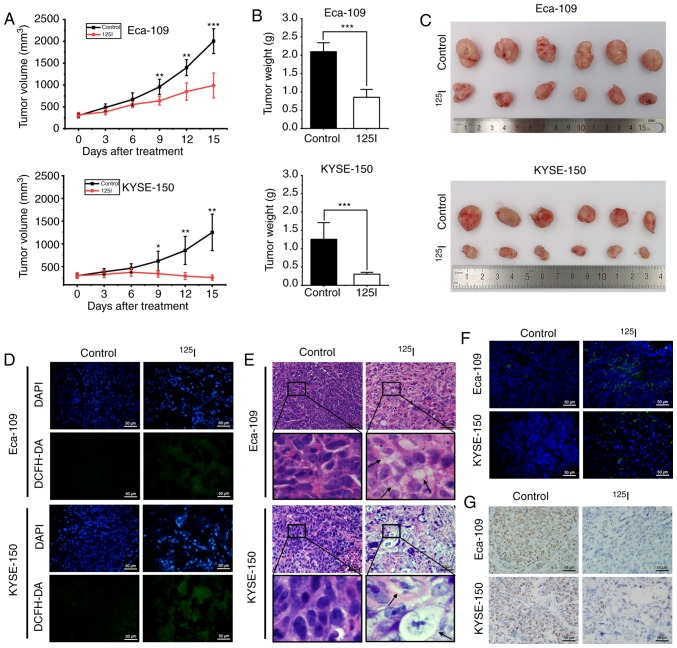
Figure 7.
125I seed radiation inhibits growth of Eca-109 and KYSE-150 esophageal cancer xenografts in mice. (A) Mice received tumor puncture (control group) or 125I seed implantation (125I seed group) when the average tumor volume reached 300 mm3. Tumor volumes were measured every three days for 15 days after treatment. (B) Weight of harvested tumors was measured 15 days after treatment. (C) Representative images of the harvested tumors. (D) Immunofluorescence detection of ROS using DCFH-DA staining (green). Tissues were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of harvested tumor specimens. Cytoplasmic vacuolation (black arrows) was observed after 125I seed implantation. Scale bar, 50 µm. (F) Representative TUNEL staining of harvested tumor specimens. Scale bar, 50 µm. (G) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of the proliferation marker, Ki-67 in harvested tumor specimen. Scale bar, 50 µm. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. control group. 125I, Iodine-125; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DCFH-DA, 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate.