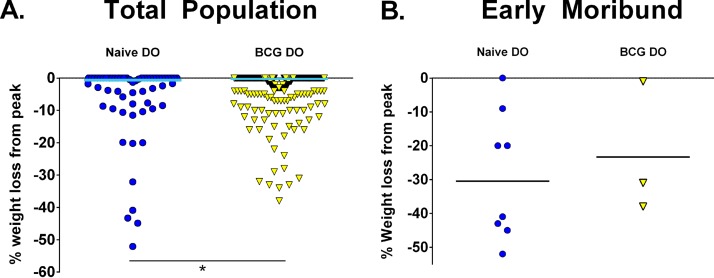
FIG 6.
BCG vaccination reduces weight loss in DO mice compared to naive mice, but weight loss does not predict morbidity. Groups of female B6 and DO mice were vaccinated subcutaneously with 105 M. bovis BCG, and control mice were sham vaccinated with PBS. Mice were aerogenically challenged with ∼45 CFU M. tuberculosis. Mice were weighed a week prior to aerosol challenge and weekly after challenge until the end of the experiment at 14 weeks after challenge. Mice that showed signs of distress were weighed daily. The percentage of weight loss from peak was calculated using the final weight (or final weight before euthanasia) divided by the peak body weight, and that value was subtracted from 100. (A) Data represent combined results from five independent experiments similar in design, where the total numbers of animals for each group are 35 naive B6 mice, 60 naive DO mice, 30 BCG-vaccinated B6 mice, and 240 BCG-vaccinated DO mice. (B) The percentage of weight loss from peak for all mice that succumbed to M. tuberculosis challenge before 14 weeks is shown; these results include data from eight naive DO mice and three BCG-vaccinated DO mice. *, differences between the groups indicated by the lines were significant (unpaired t test, P < 0.05).