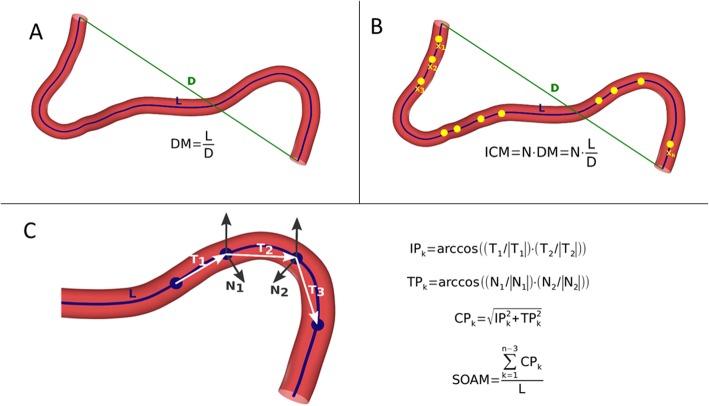
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustration of the algorithms used to calculate tortuosity metrics as described by Bullitt et al. Distance Metric (DM) provides a ratio between the actual path length of a meandering curve (L, blue centerline) and the linear distance (D, green straight line segment) between the endpoints (a). Inflection count metric (ICM) is calculated by counting the inflection points, so those points where the curve changes from convex to concave (highlighted as yellow dots in the picture). The number of inflection points (N) is normalized by multiplying it by the DM (b). Sum of angles metric (SOAM) is assessed by subdividing the arterial centerline into small segments (T1-3, white arrows) and summing the in-plane (IPk) and torsional angles (TPk) between these segments (c)