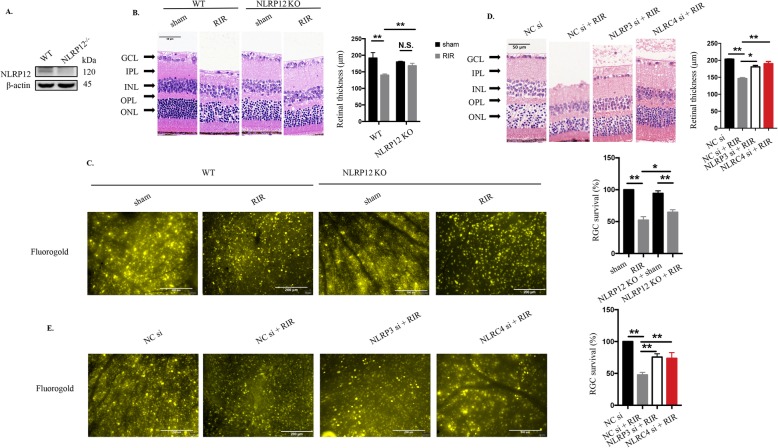
Fig. 2.
Genetic deletion of NLRP12 and inhibition of NLRP3 or NLRC4 significantly attenuate retinal damage and improve RGC survival. a Western blot detection of NLRP12 in retinas from NLRP12-deficient mice (n = 6). b HE staining and quantitative measurement of total retinal thickness targeting retinal tissue morphology in WT and NLRP12 KO mice under high IOP (n = 6). Scale bar: 50 μm. c Retrograde FG labeling and RGC amount evaluation in WT and NLRP12 KO mice under high IOP (n = 6). Scale bar: 200 μm. d HE staining and quantitative evaluation of total retinal thickness in retinal tissue subjected to high IOP followed by NLRP3/NLRC4 knockdown (20 μΜ, n = 6). Scale bar: 50 μm. e Retrograde FG labeling and quantitative measurement of RGC survival in retinal tissue subjected to elevated IOP followed by NLRP3/NLRC4 knockdown (20 μΜ, n = 6). Scale bar: 200 μm. WT: wide type; KO: knockout; RIR: retinal ischemia-reperfusion; GCL: ganglion cell layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer. All of the data are representative of at least three independent experiments. The data are represented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA.