Figure 1.
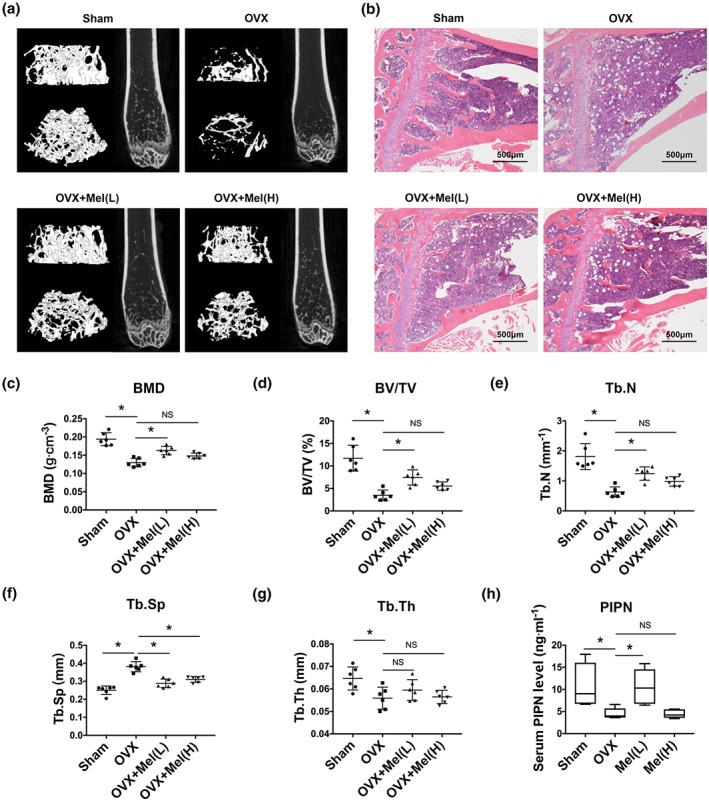
Melatonin stunted bone loss and increased bone formation in osteoporotic mice. (a–b) μCT imaging of distal femurs (a) and H&E staining (40×) of proximal tibias (b) of ovariectomy (OVX) mice followed by melatonin treatment for 6 weeks, L = low dose (10 mg·kg−1 body weight per day); H = high dose (100 mg·kg−1 body weight per day). (c–g) Bone microstructure parameters such as bone mineral density (BMD, c), trabecular bone volume per total volume (BV/TV, d), trabecular bone number (Tb. N, e), trabecular bone separation (Tb. Sp, f), and trabecular bone thickness (Tb. Th, g) were measured by μCT scanning. (h) The bone formation marker N‐terminal propeptide of type I procollagen (PINP) level in serum was detected by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD and n = 6 in each group; *P < .05, significant differences between each indicated group. NS, not significant
