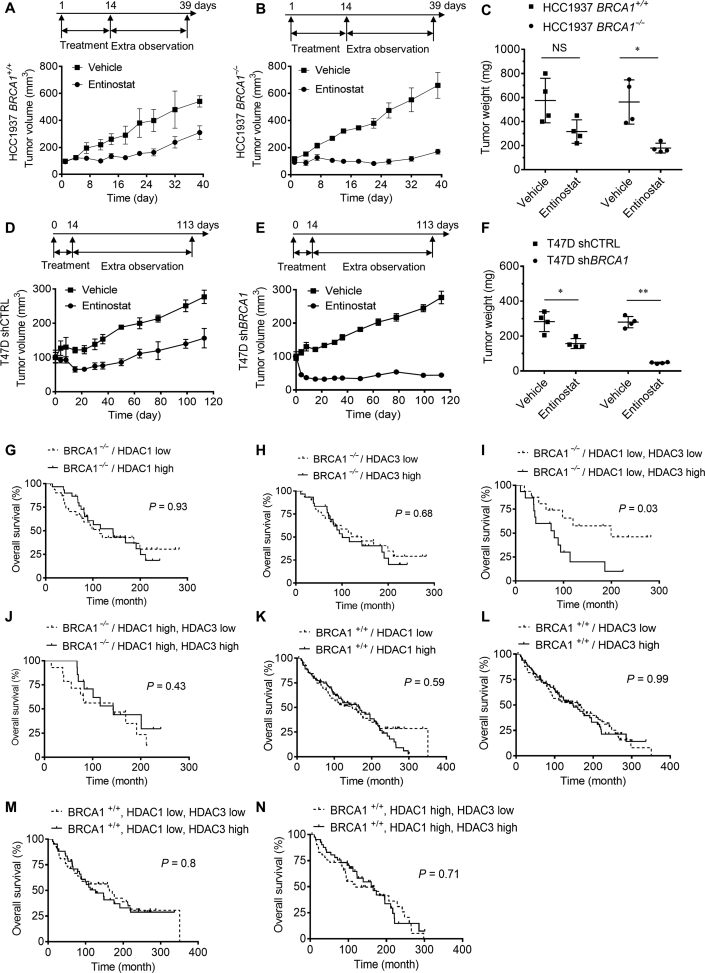
Figure 2.
In vivo synthetic lethality between HDAC inhibition and BRCA1 deficiency. (A)–(C) The effect of entinostat on the tumor growth of HCC1937 BRCA1 isogenic cancer was tested. SCID/NOD mice bearing HCC1937 BRCA1+/+ (A) or BRCA1−/− (B) tumor were given vehicle or entinostat (10 mg/kg) for 14 days and tumor volume was measured until the end of the experiment. Tumor wet weight was measured at the end of the xenograft experiments (C) (n = 5). (D)–(F) The effect of entinostat on the tumor growth of HCC1937 BRCA1 isogenic cancer was tested. Nude mice bearing T47D shCTRL (D) or shBRCA1 (E) tumor were given vehicle or entinostat (10 mg/kg) for 14 days and tumor volume was measured until the end of the experiment. Tumor wet weight was measured at the end of the xenograft experiments (F) (n = 4). (G)–(N) The effect of BRCA1 status and HDAC1/3 expression on breast cancer patient survival was analyzed using the clinical data from the METABRIC. The patients were sub-grouped according to the BRCA1 mutation status and the expression levels of HDAC1 and 3, and the overall survival from each subgroup was analyzed. Data are mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 between two groups.