Fig. 1.
Overview of this invited review.
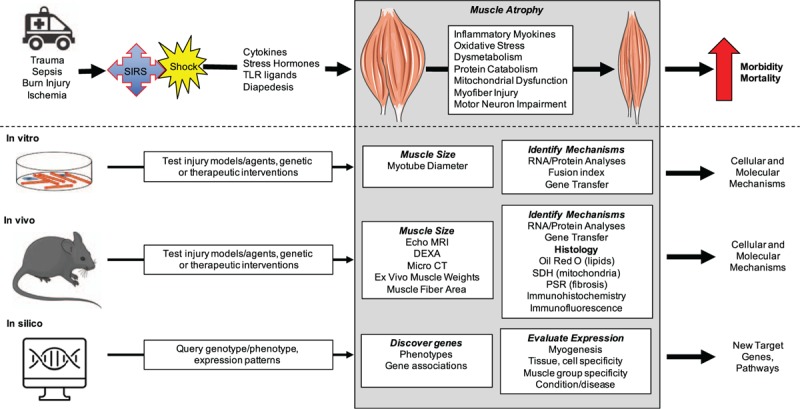
Trauma leads to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and shock, which produces mediators that act on muscle to produce atrophy through effects on multiple processes affecting the myofibers but also the motor neurons. This leads to morbidity and mortality. We review methods to interrogate the mechanisms underlying this injury-induced atrophy using cell culture, mouse models, and available datasets. CT indicates computed tomography; DXA, dual energy x-ray absorptiometry, PSR, picrosirius red; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; TLR, toll-like receptor.
