Figure 3.
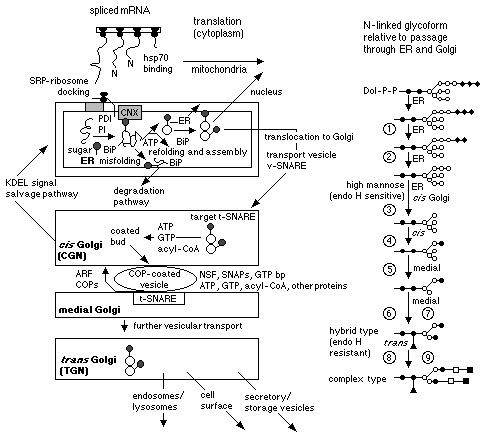
Intracellular protein translation and cisternal transport. Cytoplasmic translation results in a nascent polypeptide that is chaperoned by the hsp70 protein, which may direct the ribosome‐peptide complex to the mitochondrion or the ER upon N‐terminal peptide signaling. A signal‐recognition particle (SRP) binds to the signal sequence, halting translation until it has docked at the SRP receptor. The hsp70 protein maintains the protein in a translocation‐competent state, enabling membrane protrusion. Inside the ER the protein undergoes refolding assisted by protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), BiP, and calnexin (CXN). Initial N‐glycosylation takes place cotranslationally in the ER. Misfolded protein, associated with BiP, is retained and eventually degraded. Transport of folded, assembled protein between the ER and Golgi cisternae occurs through a series consisting of budding, vesicle formation, and specific binding to target cisternae surfaces, through to the trans Golgi (TGN), where distribution to particular destinations occurs. Abbreviations: ARF, ADP‐ribosylation factor; COPs, a family of coat proteins; Dol, dolichol; endo H, endoglycosidase H; GTP bp, GTP binding protein; NSF, NEM‐sensitive cytosolic factor (identical to yeast sec 18p); SNAPs, three soluble NSF attachment proteins; v‐SNARE and t‐SNARE, SNAP receptors. Symbols: solid circles, N‐acetyl glucosamine; open circles, mannose; solid diamonds, glucose; open squares, galactose; solid squares, sialic acid; solid triangles, fucose; circled 1, α‐glucosidase I; circled 2, α‐glucosidase II; circled 3, α‐1,2‐mannosidase; circled 4, GlcNAc transferase I; circled 5, α‐mannosidase II; circled 6, GlcNAc transferase II; circled 7, α‐1,6‐fucosyl transferase; circled 8, β‐1,4‐galactose transferase; and circled 9, α‐2,3‐sialyl transferase.
