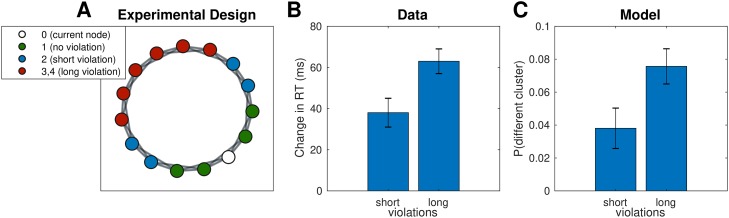
Fig 8. Slower reactions to cross-cluster transitions.
A. Graph used in Lynn et al. [12]. Each node (white) is connected to its neighboring nodes and their neighbors (green). Blue nodes are 2 transitions away from the white node, while red nodes are 3 or 4 transitions away. B. Results from Lynn et al. [12] showing that, on the test trial, participants were slower to respond to long violations than to short violations. Change in RT is computed with respect to average RT for no-violation transitions. Error bars are s.e.m (78 participants). RT, reaction time. C. Results from simulations showing that long violations are more likely to end up in a different cluster, which would elicit a greater surprise and hence a slower RT, similar to crossing a cluster boundary.