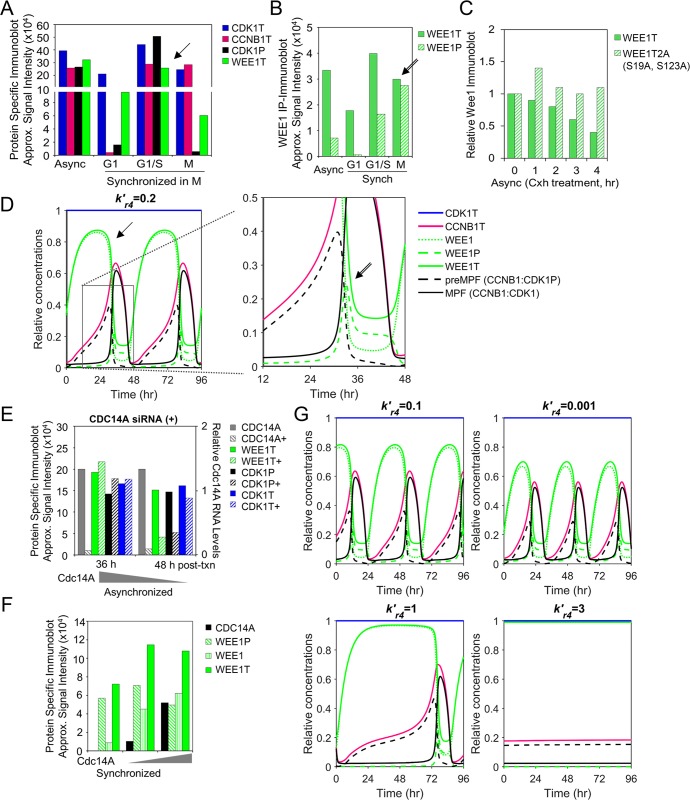
Fig 3. WEE1-mediated regulation of preMPF and MPF oscillations.
(A) Approximated steady-state protein levels from studies by Ovejero et al. [8] using immunoblot analysis for CDK1T, CCNB1T, WEE1T and CDK1P Y15 (i.e. preMPF) in WEE1-expressing U2OS cells following release from synchronization in M phase. Arrows mark points of comparison between in vitro and in silico data. (P, phosphorylated protein; T, total protein) (B) Levels of WEE1P (S139) observed in immunoprecipitated WEE1T from studies by Ovejero et al. [8] as described in (A). (C) Approximated changes in protein levels for WEE1T and mutated unphosphorylated WEE1T 2A (S139A, S123A) during cycloheximide treatment by Ovejero et al. [8]. (D) Simulation of phosphatase activity (PPase, ) in regulating free WEE1, WEE1P and WEE1T with associated oscillations in CDK1T, CCNBT, preMPF (CCNB1:CDK1P), and active MPF kinase (CCNB1:CDK1) over the indicated time periods. Boxed area is magnified. (E) Disrupting relationships by siRNA-mediated reduction of phosphatase CDC14A (+) in asynchronized U2OS cells and associated changes in levels of WEE1T and CDK1P Y15 (i.e. preMPF) compared to control by Ovejero et al. [8]. (F) Approximated changes in WEE1, WEE1T and WEE1P levels upon increasing expression of CDC14A phosphatase as demonstrated by Ovejero et al. [8]. (G) Simulated decrease in phosphatase (PPase, i.e. CDC14A) activity () and associated changes in protein concentrations and mitotic oscillations of CDK1T, CCNBT, WEE1, WEE1T, WEE1P, preMPF (CCNB1:CDK1P), and active MPF kinase (CCNB1:CDK1). In contrast, simulated increase in PPase activity () and associated changes resulting in a mitotic collapse with no active MPF kinase (CCNB1:CDK1) over 96 hr.