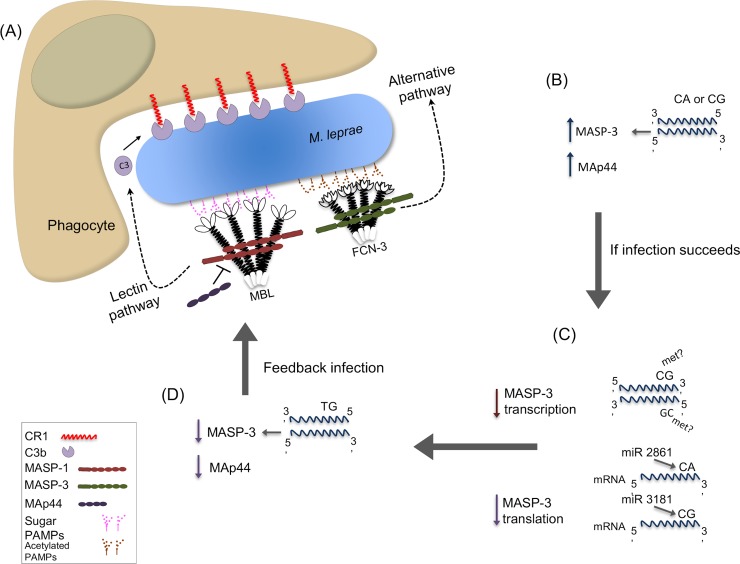
Fig 6. Proposed roles for MASP1 products and polymorphisms in susceptibility to M. leprae infection.
(A) Collectins (e.g. MBL) or ficolins (e.g. FCN-3) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), composed of sugar/acetylated groups on M. leprae. MASP-2 (not depicted in this image) and MASP-1 homodimers complexed with them activate the lectin pathway of complement, whereas MASP-3 may activate the alternative pathway. Both pathways lead to C3b-opsonization and CR1-mediated internalization of the pathogen. (B) Healthy individuals with rs1109452 and rs850314 CA or CG haplotypes express higher MASP-3 levels. Higher MASP-3 and MAp44 levels were also associated with resistance against the disease. (C) CpG methylation at the CG haplotype in exon 12 may impair mRNA transcription, spliceosome assembly and mRNA processing. Reduced MASP-3 levels may also result from the differential recognition of CA and CG haplotypes by miRNAs (miR-2861 and miR-3181, respectively). (D) Individuals with TG haplotypes present lower baseline MASP-3 levels. Lower MASP-3 and MAp44 levels seem to predispose to the infection, possibly by optimizing opsonin coverage of the parasite.