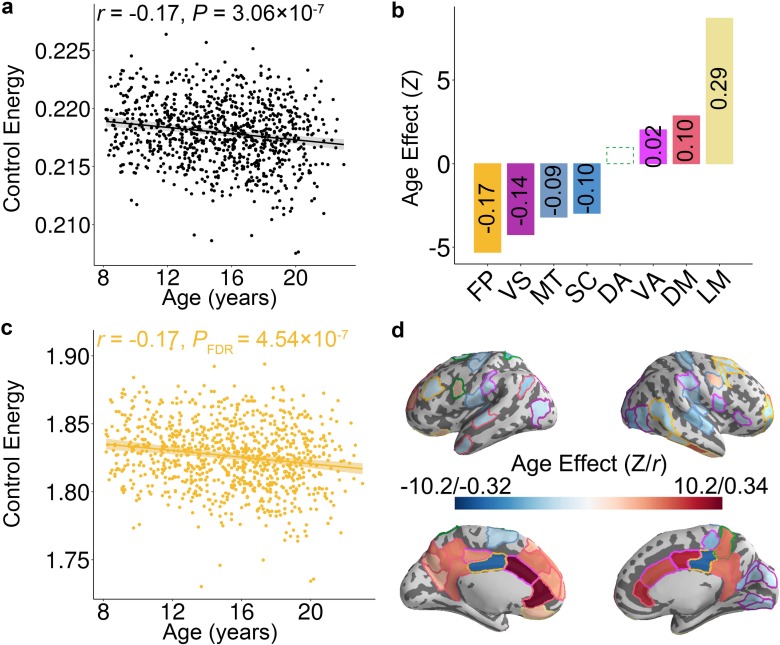
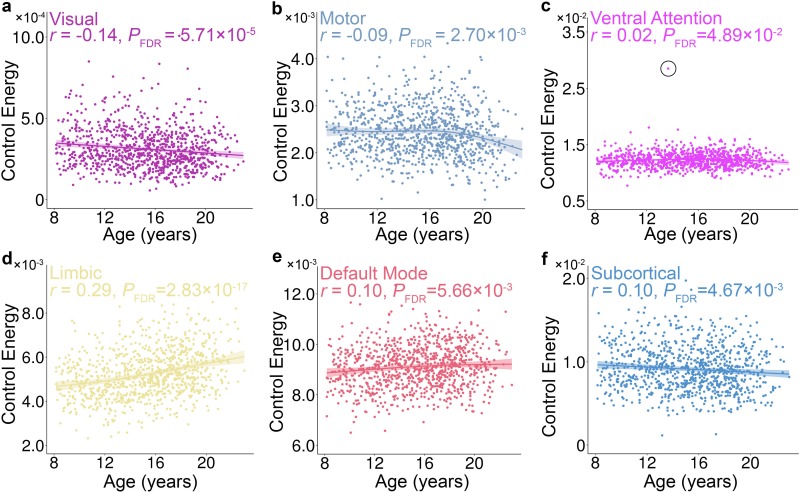
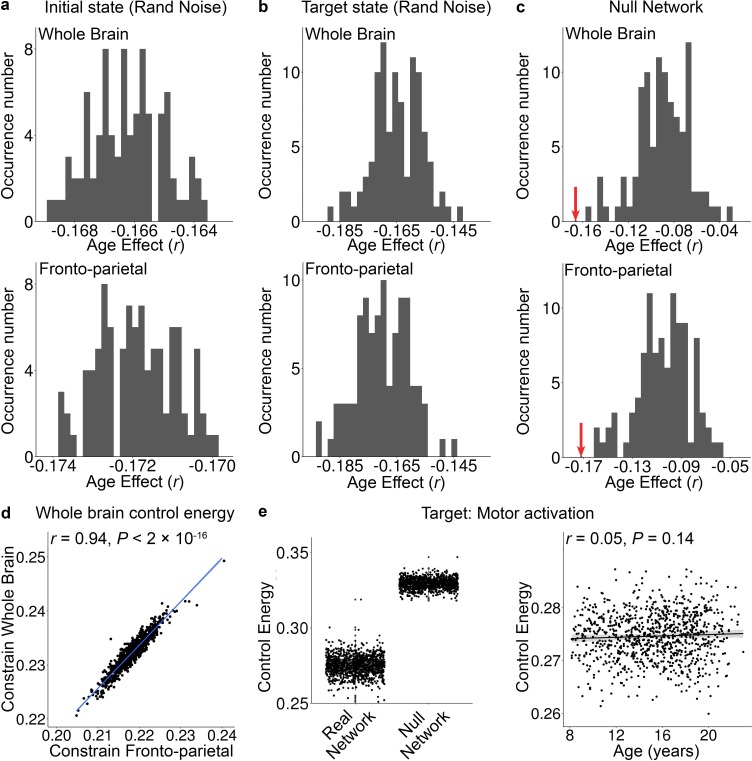
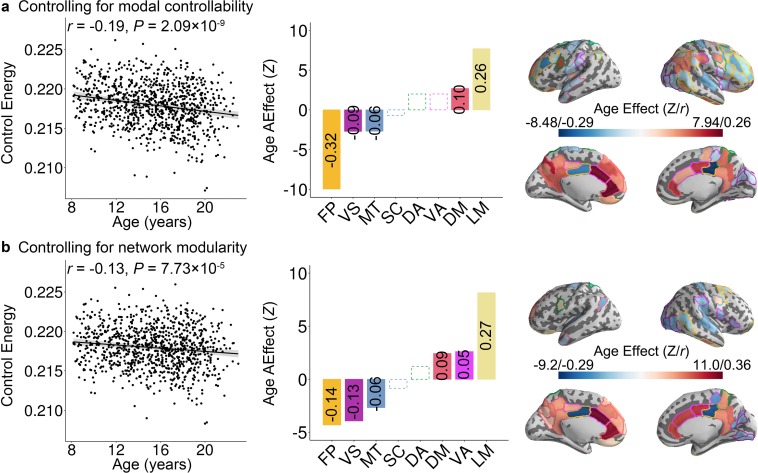
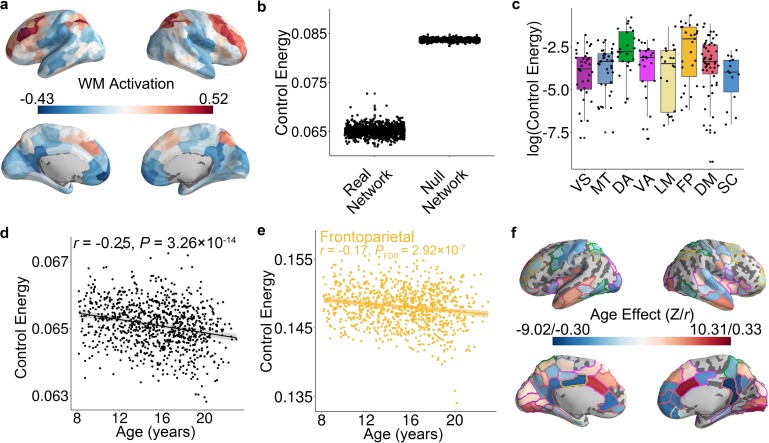
Figure 2. Control energy evolves with age in youth.
(a) The mean whole-brain control energy required to reach the fronto-parietal activation target declines with age. (b) Control energy declines significantly with age in the fronto-parietal, visual, motor and subcortical systems. In contrast, control energy increased in the ventral attention, default mode and limbic systems. For each system with a significant association, the effect size is reported (in each bar) as the partial correlation between system-level control energy and age while controlling for the covariates. There is one outlier in the scatter plot of ventral attention system (Figure 2—figure supplement 1c) and the age-related changes of control energy was not significant (p=0.11) in this system after removing the outlier. (c) The control energy of the fronto-parietal system declines significantly with age. (d) The age effect of control energy for each brain region. The color of the contour of each brain region represents the cognitive system for each region (see Figure 1—figure supplement 2). In the scatterplots shown in panels (a and c), data points represent each subject (n = 946), the bold line indicates the best fit from a general additive model, and the shaded envelope denotes the 95% confidence interval. It should be noted that Z value was derived from the general additive model, which captures both linear and nonlinear relationships; the partial correlation reflects only linear relationships. VS: visual; MT: motor; DA: dorsal attention; VA: ventral attention; LM: limbic; FP: fronto-parietal; DM: default mode; SC: subcortical.