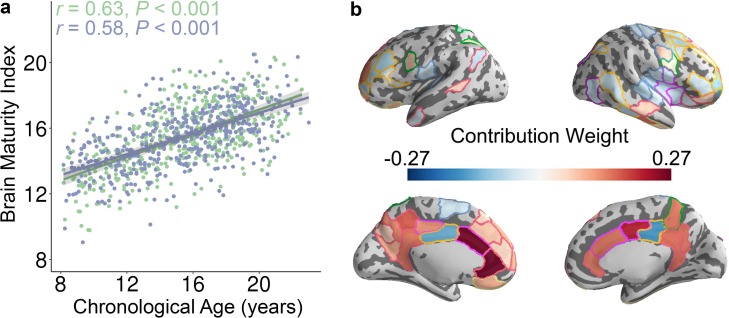
Figure 3. The whole-brain control energy pattern contains sufficient information to predict brain maturity in unseen individuals.
(a) The predicted brain maturity index was significantly related to the chronological age in a multivariate ridge regression model that used 2-fold cross validation (2F-CV) with nested parameter tuning. The complete sample of of subjects was divided into two subsets according to age rank. The blue color represents the best-fit line between the actual score of the first subset of subjects and their scores predicted by the model trained using the second subset of subjects. The green color represents the best-fit line between the actual score of the second subset of subjects and their scores predicted by the model trained using the first subset of subjects. (b) Regions with the highest contribution to the multivariate model aligned with mass-univariate analyses and included frontal, parietal, and temporal regions. We displayed the 79 regions with the highest contribution, to facilitate comparisons with mass-univariate analyses (where there were 79 regions with significant age effects).