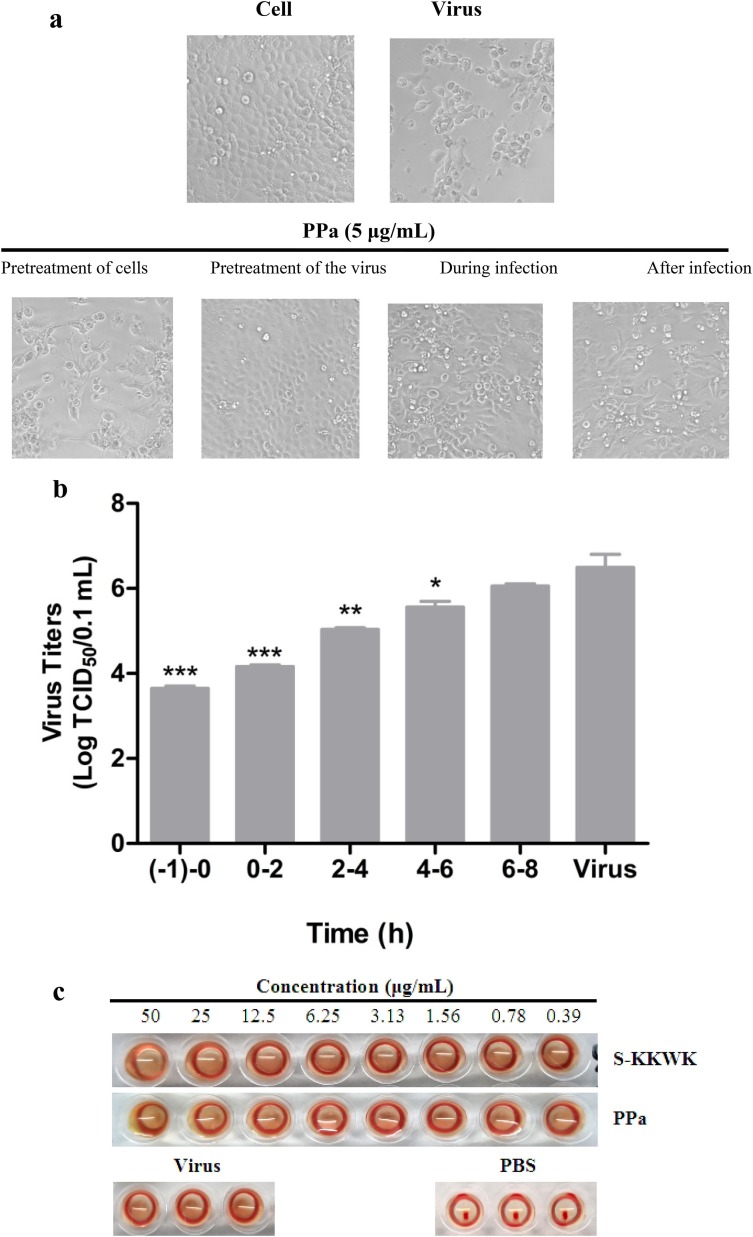
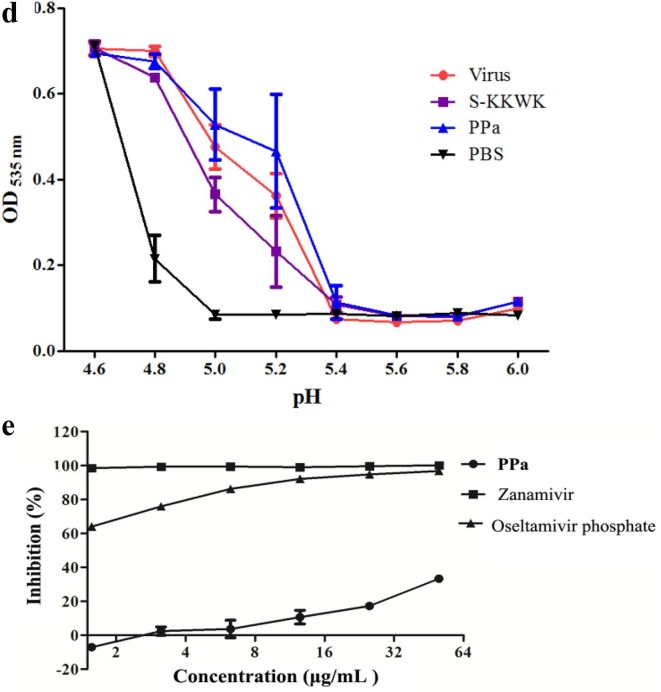
Fig. 3.
a Cytopathic effects (CPE) on MDCK cells infected with influenza A/PR/8/34 (H1N1) (100 TCID50). Four different drug administration protocols were employed to treat the virus or cells at the concentration of 5 μg/mL of PPa. Phase contrast images were obtained using a microscope at 48 h post-infection. 3b Time-of-addition assay. MDCK cells infected with A/PR/8/34(H1N1) (100 TCID50) were treated with 5 μg/mL PPa at the indicated time intervals. The virus titer was determined by measuring the TCID50 of virus in the supernatant at 48 h post-infection; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. 3c Hemagglutinin inhibition assay designed to measure the inhibitory effect of PPa on the binding of the virus to target cells. An equal volume of influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/34(H1N1) virus (4HAU) was transferred to a microwell plate containing two-fold serially diluted PPa in PBS. Then, erythrocytes (1% v/v in saline) were added to each well. After an incubation at room temperature for 1 h, the hemagglutination reaction was analyzed. PBS without virus served as a positive control, while virus served as the negative control. 3d Hemolysis inhibition assay. A suspension of freshly prepared chicken erythrocytes (2%) was added to the mixture of PPa (15 μg/mL) with the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 (H1N1) in allantoic fluid. The mixture was then acidified to a pH ranging from 4.6 to 6.0 (sodium acetate, 0.5 M), and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. At the end of the incubation, the mixture was centrifuged and the absorbance of the supernatants containing released hemoglobin was measured at OD535using a Multiskan FC microplate reader. 3e Neuraminidase (NA) inhibition assay. A reaction mixture consisting of PPa and influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/34(H1N1) virus in MES buffer was incubated for 45 min. Afterwards, 4-MU-NANA was added to each well, the mixture was incubated for another 1 h, and the reaction was terminated with NaOH (83% ethanol). Finally, an excitation wavelength of 340 nm and an emission wavelength of 440 nm were used to measure resulting fluorescence of the mixture. Oseltamivir phosphate and zanamivir were employed as positive controls.