Figure 1.
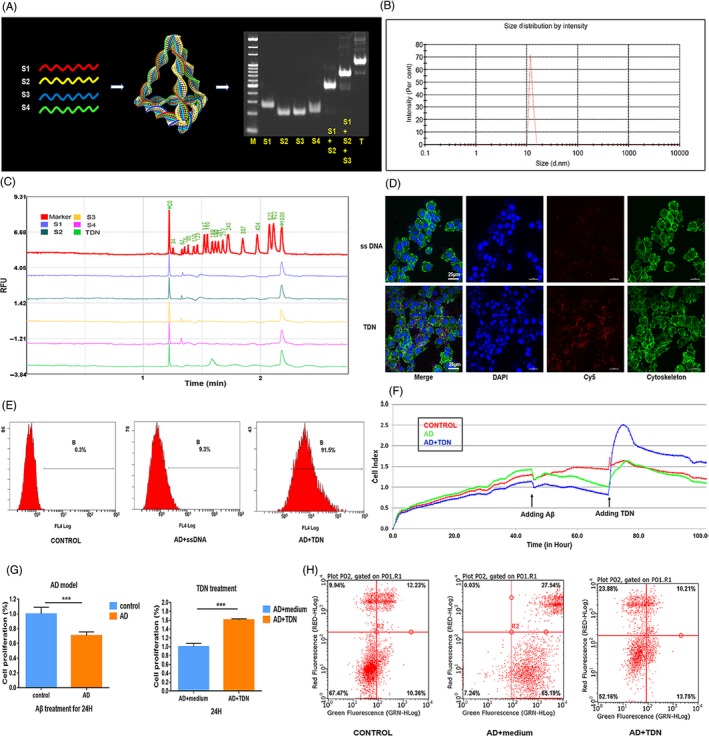
Therapeutic effect of tetrahedral DNA nanostructures (TDN) on an Alzheimer's disease PC12 cell model. A, Sketch map of TDNs and confirmation of the successful synthesis of TDNs by native PAGE (M: marker, S: single‐stranded DNA, T: TDN). B, Confirmation of the successful synthesis of TDNs by capillary electrophoresis. C, Confirmation of the successfully assembled TDNs by dynamic light scattering. D, Cellular uptake of Cy5‐TDNs and Cy5‐single‐stranded DNA in Alzheimer's disease cell model (cytoskeleton: green; nucleus: blue; Cy5: red). Scale bars are 25 µm. E, Cellular uptake of TDNs by flow cytometry. F, Cellular proliferation reaction detected by real‐time cell analysis system (RTCA). Statistical analysis of RTCA results. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 4). Student's t test: ***P < .001. G, Analysis of apoptosis in an Alzheimer's disease PC12 cell model upon exposure to tetrahedral DNA nanostructures (TDNs; 250 nmol/L) by flow cytometry. H, Addition of TDNs significantly reduced the proportion of apoptotic cells in the Alzheimer's disease cell model, indicating that TDNs can inhibit apoptosis to a certain extent
