Figure 7.
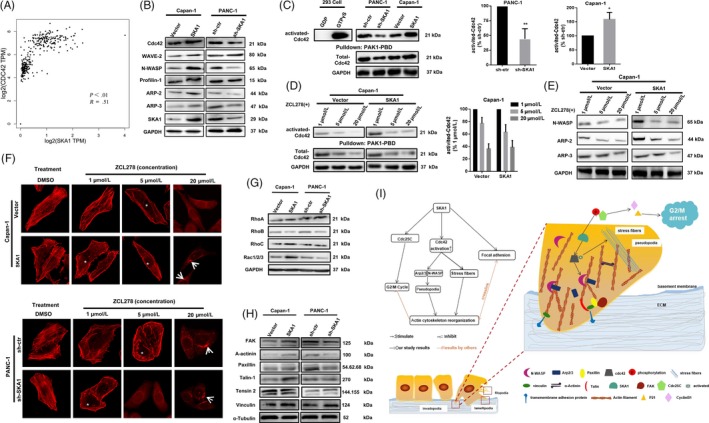
SKA1 remodels actin cytoskeleton via activating Cdc42. A, Pearson's correlation test was used to analyse the correlation between the expression level of SKA1 and Cdc42 according to TCGA database (R = .51, P < .01). B, Immunoblotting performed in PANC‐1 and Capan‐1 cells’ infectants to verify the proteins that regulate actin cytoskeleton. C, Cdc42‐GTP pull‐down and Western blot analyses of the activation state of Cdc42 expression and total expression of Cdc42 in the indicated cells. D and E, The application of ZCL278 resulted in a dose‐dependent decrease in Cdc42 activity, followed by inhibition of endogenous Arp2/3, N‐WASP. F, Cells were fixed and stained with rhodamine‐phalloidin to label filamentous actin following ZCL278 treatments. Results showed that ZCL278 inhibits microspike formation and stress fibres in PANC‐1 and Capan‐1 cells. White asterisks indicate the subcellular locations that normally show stress fibre distribution. White arrows point to the seemingly disruption Golgi organization. G, RhoA, RhoB, RhoC and Rac1/2/3 protein expression were detected, and only a total of Rac1/2/3 increase accompanied by SKA1 overexpression was observed. H, FAK, Talin and ɑ‐actinin levels increased with SKA1 expression in Capan‐1 cells, FAK, Paxillin and ɑ‐actinin levels decreased with SKA1 knockout in PANC‐1 cells. I, Proposed mechanistic scheme of SKA1 in promoting tumour progression in PDAC
