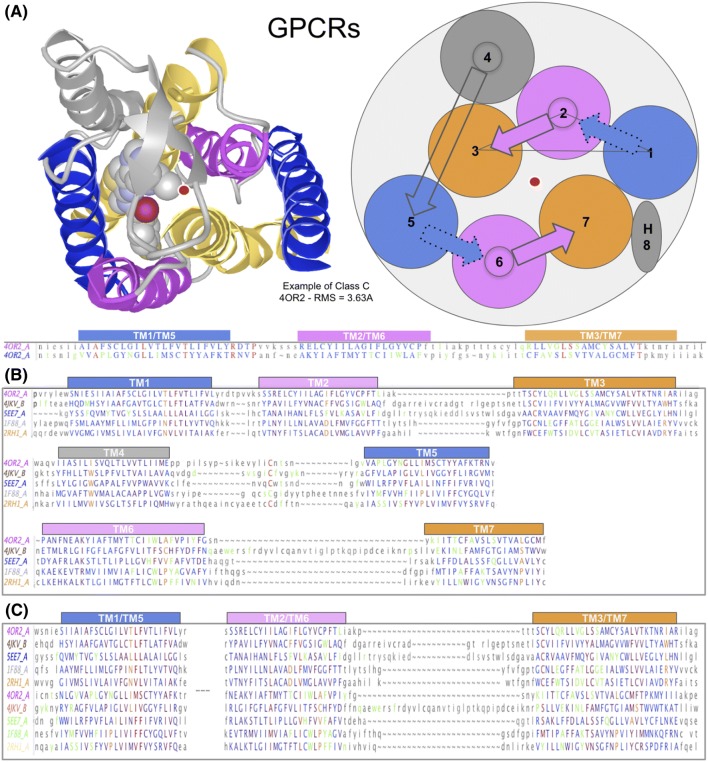
Fig. 3.
GPCR classes A, B, C, F structure-based domains and protodomains sequence alignments. a Structure of a GPCR with a 3D representation and a 2D representation, seen from the extracellular side. b Multiple domain alignment for classes C, A, C and F (RMSD relative to 4OR2.A: 4JKV.A: 3.06 Å, 5EE7.A: 2.91 Å, 1F88: 3.21 Å, 2RH1: 3.09 Å. c Multiple protodomains alignment: TMH-123 vs. TMH-567—RMSD relative to the first protodomain (4OR2.A-1) used as a reference structure in the alignment: 3.63 Å (4OR2.A-2), 2.12 Å (1F88.A-1), 3.29 Å (1F88.A-2), 1.73 Å (5EE7.A-1), 2.77 Å (5EE7.A-2), 1.93 Å (4JKV.A-1), 2.55 Å (4JKV.A-2), 1.79 Å (2RH1.A-1), 3.59 Å (2RH1.A-2), respectively, for class C (4OR2, human metabotropic glutamate receptor 1: GRM1), class A (1F88, bovine rhodopsin: OPSD and 2RH1, human β2 adrenergic receptor: ADRB2), class B (5EE7, human glucagon receptor: GCGR), class F (4JKV, human smoothened receptor: SMO). Similarity scale from blue least similar to red (most similar). In green: ligand proximal residues (at less than 4 Å distance) when a ligand is present in the crystal structure. In orange, the most conserved residue positions in class A (1.50 N, 2.50 D, 3.50 R, 4.50 W; not shown, 5.50 P, 6.50 P, and 7.50 P) and their counterparts in other classes