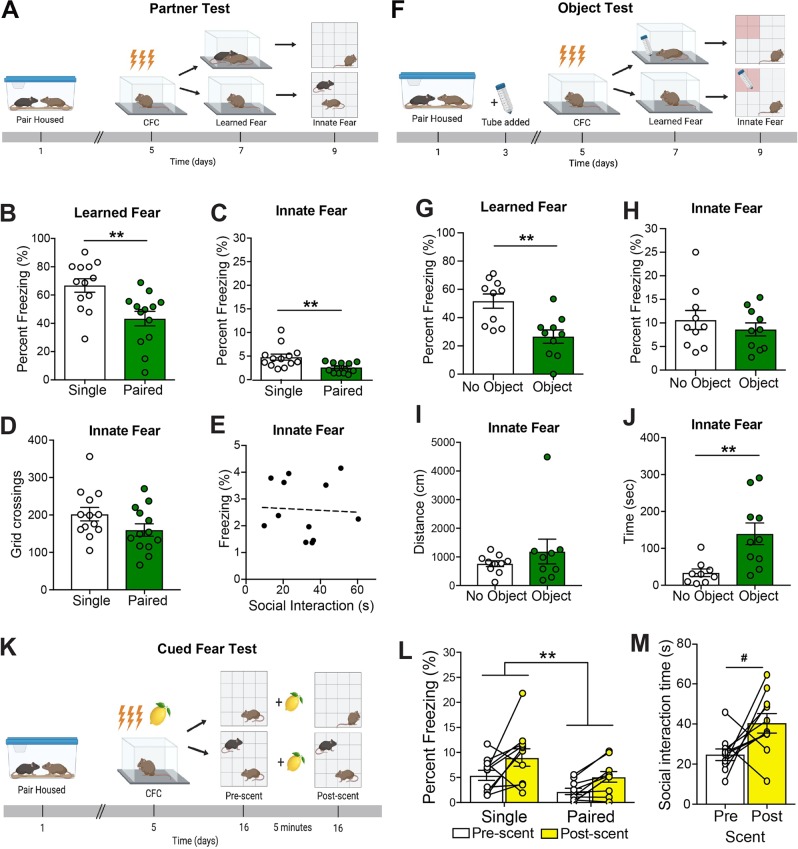
Fig. 1. Cagemate presence reduces freezing in multiple fear-provoking tests.
a Timeline and behavioral schematic of testing with or without a cagemate. Learned fear was assessed by measuring freezing upon re-exposure to a context previously paired with an aversive shock, whereas innate fear was assessed in an anxiogenic novel environment. b Mice re-exposed to an aversive context with their cagemate showed lower levels of freezing when compared with mice tested alone. c Similar to learned fear, mice froze less in an innate fear context when tested with their cagemate present compared with mice tested alone. d Mice with and without their cagemate show similar locomotive behavior in the innate fear context. e There is no correlation between time investigating the cagemate and time freezing in the innate context for paired mice. f Timeline and behavioral schematic of testing with or without an object. g Mice re-exposed to an aversive context with a novel object showed lower levels of freezing when compared to mice tested alone. h Mice show similar freezing in an innate fear context when tested with a novel object present compared with mice tested alone. i Mice with and without an object show similar locomotive behavior in the innate fear context. j Mice spent more time in the object zone if the object was present. k Timeline and behavioral schematic showing aversive cue exposure with (bottom) or without (top) a cagemate present. After receiving a shock with a lemon scent present, mice were exposed to a novel context for 5 min and then the lemon scent (cue) was added to the arena for another 5 min. The lemon scent was the only shock-associated cue present in the test. l All mice increased their freezing levels after presentation of the lemon scent, but cagemate presence reduce freezing before and after scent presentation relative to mice tested alone. m Paired mice showed a trend towards increased interaction with their cagemate after the scent (fear cue) was added to the chamber. n = 10–13 mice per group. Error bars represent ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, #p = 0.055 CFC, contextual fear conditioning.